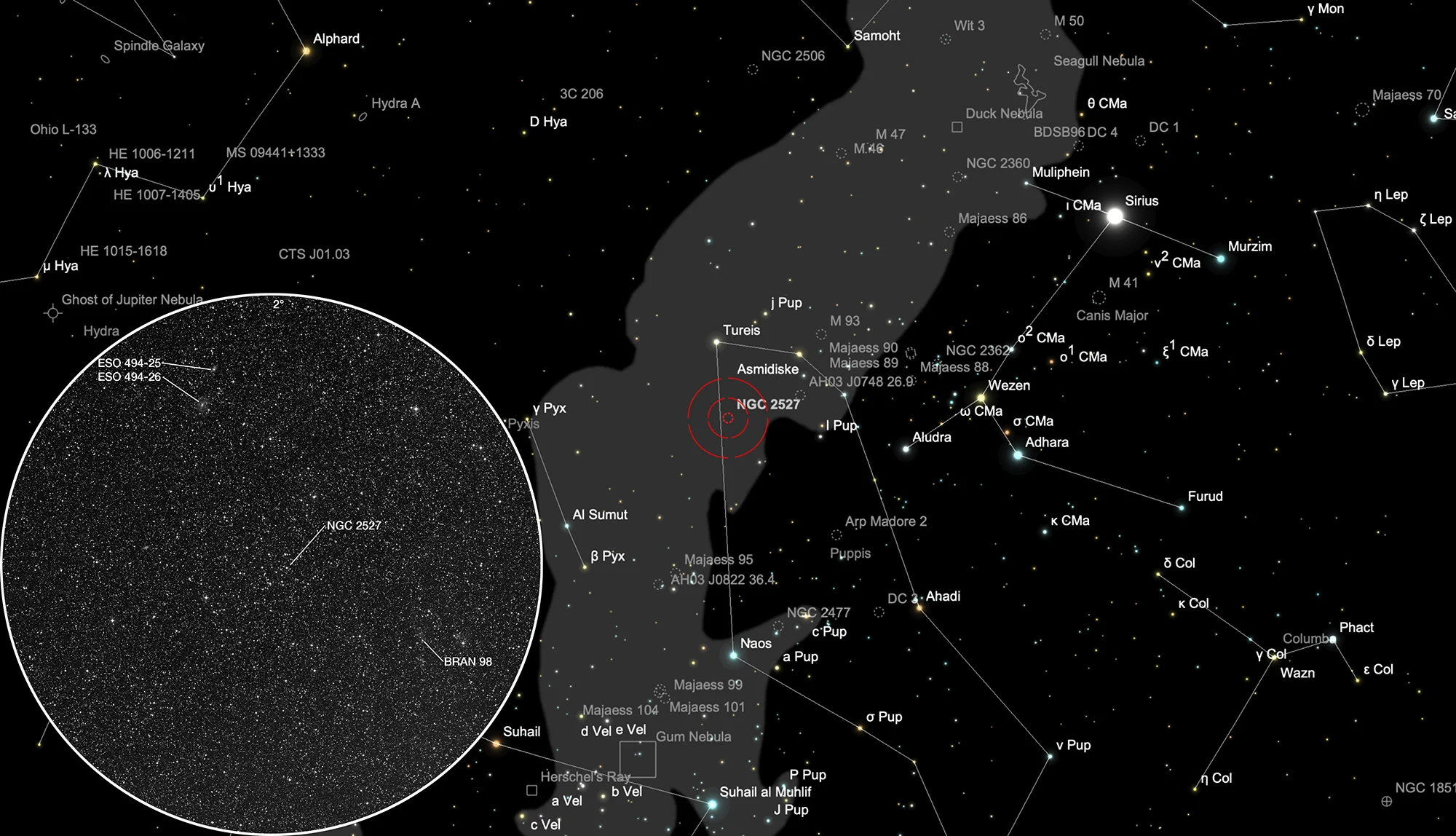
Open Cluster NGC 2527

History
This open cluster was discovered by William Herschel on 9 December 1784 using his reflecting telescope of 18.7 inch aperture and 20 feet focal length. He listed it as VIII 30 with the notes: «A very large cluster of many coarsely scattered large stars.» [463]
John Herschel observed this cluster first on 7 January 1831 from Slough, England, listed it as h 488, and noted: «Cluster pretty rich; very coarsely scattered; fills field; stars 10...15 magnitudes.» [466] Few years later while in South Africa he observed the cluster again on 5 February 1837 and listed it as h 3112 and noted: «Cluster 7th cclass, distinguished among milky way clusters; pretty rich; bright. The star taken is the chief of a condensed hook in the following part.» [11] Although he identified h 3112 with h 488 (IV 30) he determined the position about 3 minutes of time to far west. Hence the cluster received two different designations in his «General Catalogue» with GC 1621 = h 3112 and GC 1624 = h 488 = VIII 30. [467] Dreyer listed GC 1621 = h 3112 as NGC 2520 and GC 1624 = h 488 = VIII 30 as NGC 2527. [313] So, NGC 2520 is a duplicate of the earlier observation NGC 2527.
Physical Properties
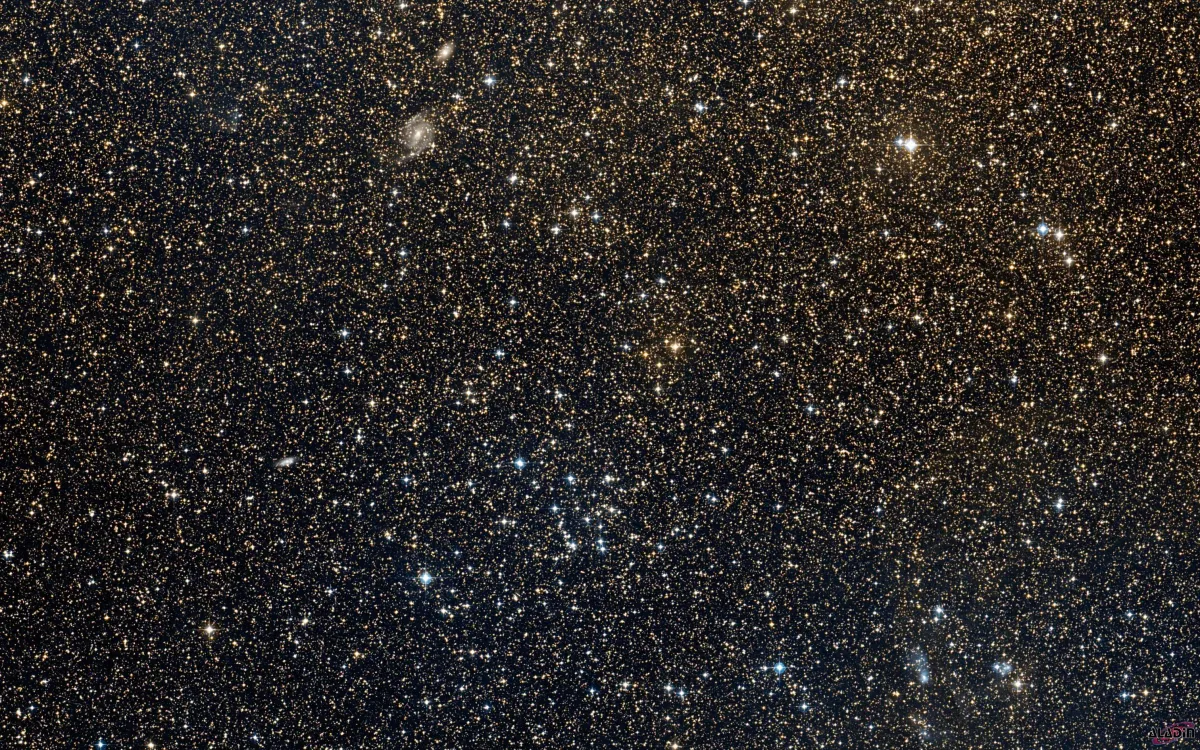
Nearby to the open cluster NGC 2527 from our perspective are two faint, distant galaxies (ESO 494-25 and ESO 494-26) and also a reflection nebula BRAN 98.
| Name | Type | RA (J2000.0) | Dec (J2000.0) | PM [mas/y] | Parall. [mas] | Rvel [km/s] | z | M Type | Size ['] | Magnitudes | Identifiers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESO 494-25 | PaG | 08h 05m 59s | -27° 23' 51" | 963.3 | 0.003218 | 0.2 | 1.357 × 0.733 | B 13.45; R 12.6; I 12.7; J 9.441; H 8.682; K 8.358 | 2MASX J08055927-2723510; CGMW 2-2203; ESO 494-25; ESO-LV 494-0250; FI 13; HIPASS J0806-27a; IRAS 08039-2715; LEDA 22736; PSCz P08039-2715; RR95 159a; SGC 080355-2715.1; ZOAG G245.57+02.45; [DB76] 430-2 | ||
| ESO 494-26 | GiG | 08h 06m 11s | -27° 31' 42" | 0.149 | 964.17 | 0.003221 | 3.0 | B 12.47; G 17.374298; R 10.84; J 8.905; H 8.206; K 7.876 | 2MASX J08061109-2731422; AGC 25934; AM 0804-272; CGMW 2-2212; ESO 494-26; ESO-LV 494-0260; Gaia DR2 5693982214690237568; Gaia DR3 5693982214690237568; HIZOA J0806-27; HIZSS 32; IRAS 08041-2723; LEDA 22746; PSCz P08041-2723; RR95 159b; SGC 080407-2723.0; WB89 1092; ZOA J080610.996-273140.54; ZOAG G245.71+02.41; [CHM2007] HDC 469 J080611.09-2731422; [CHM2007] LDC 561 J080611.09-2731422; [DB76] 430-3 | ||
| NGC 2527 | OpC | 08h 05m 02s | -28° 07' 06" | -5.549 | 1.536 | 39.99 | 0.000133 | 49 × 49 | B 6.81; V 6.5 | C 0803-280; Cl Collinder 174; NGC 2527; OCl 685.0; [KC2019] Theia 1047; [KPR2004b] 180; [KPS2012] MWSC 1428 | |
| BRAN 98 | ISM | 08h 02m 30s | -28° 24' 01" | BRAN 98; IRAS 08004-2815; WB89 1088 |
Finder Chart
The open cluster NGC 2527 is located in the constellation Puppis. On 20 January it in opposition with the Sun and is therefore highest in the sky at local midnight.