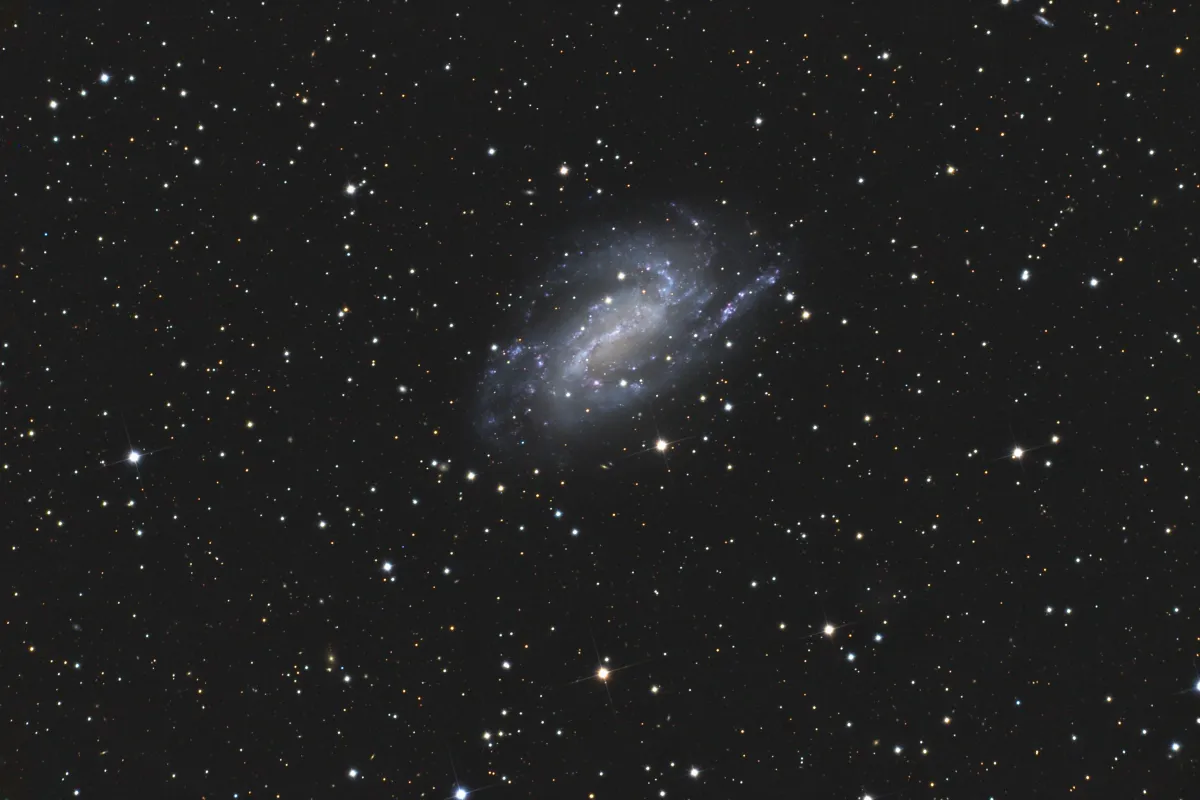
Amatha Galaxy (NGC 925)

History
The galaxy was discovered on 13 September 1784 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel with his self-made 18.7 inch f/12.8 reflecting telescope in Slough, England. He recorded it as III 177, Class III standing for very faint nebulae. He noted: «Very faint, considerably large, irregularly round, resolvable, 2 or 3' in diameter.» [463] John L. E. Dreyer entered the galaxy as NGC 925 in his «New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars» published in 1888. [313]
Physical Properties
The galaxy NGC 925 is an H-II galaxy of the morphological type SAB(s)d and has a redshift of z ≈ 0.00185, which corresponds to a distance of about 7 Mpc to 10 Mpc. It belongs to the NGC 1023 Galaxy Group. [145]
| Designation | NGC 925 |
| Type | Gx (SBcd) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 02h 27m 16.8s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +33° 34' 44" |
| Diameter | 10.5 × 5.9 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 10.7 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 10.1 mag |
| Surface brightness | 14.4 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 102° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.001845 |
| Distance derived from z | 7.79 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 8.570 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | cF, cL, E, vgbM, 2 st 13 np |
| Identification, Remarks | WH III 177; h 222; GC 542; UGC 1913; MCG 5-6-45; CGCG 504-85; IRAS 02243+3321; KARA 105; KUG 0224+333 |
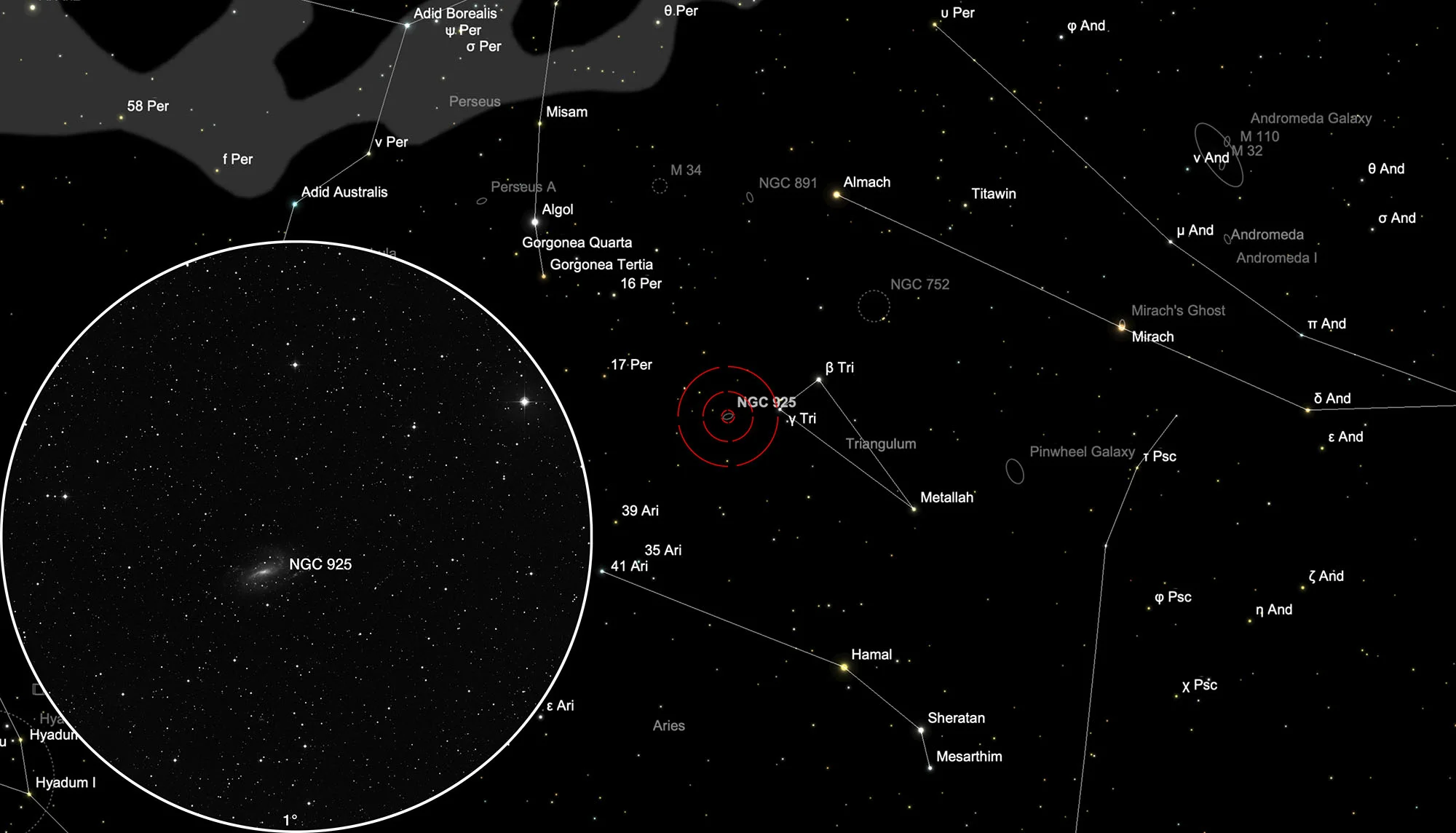
Finder Chart
The galaxy is located in the Triangulum constellation. On 2 November it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best time to observe is June to April, when it is highest at night.