Galaxies NGC 672, IC 1727 & Asterism Collinder 21

History
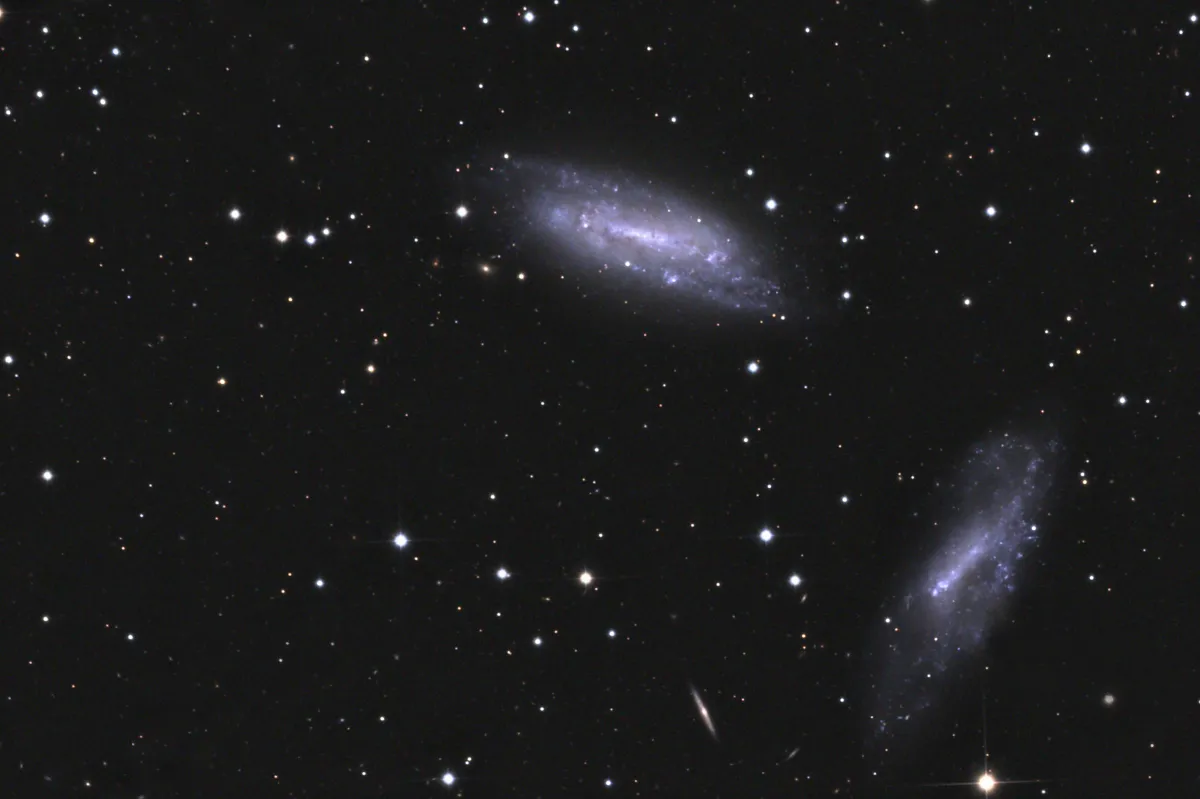
The galaxy NGC 672 was discovered on 26 October 1786 by William Herschel with his 18.7 "reflector telescope. Herschel seemed to have overlooked the neighboring galaxy IC 1727 due to its lower luminosity. It was only discovered on 29 November 1896 by Isaac Roberts with a 20" reflector telescope discovered photographically. [277]
Physical Properties
The two galaxies NGC 672 and IC 1727 are physically very close and show gravitational interaction with one another. IC 1727 shows a strong asymmetry in the apparent distribution of young stars, while that of older stars is more even. The galaxy NGC 672 shows no asymmetry in the distribution of stars of different ages. The distance from NGC 672 is estimated at 7.22 ± 0.10 Mpc and that from IC 1727 at 7.14 ± 0.10 Mpc. It is estimated that star formation in the two galaxies occurred in two intervals 20-30 and 450-700 million years ago. [426]
The galaxy NGC 684 was discovered by William Herschel on the same night as NGC 672. [277]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 672 | 01 47 54.0 | +27 25 58 | Gx (SBc) | 11.5 | 10.9 | 0.6 | 13.9 | 6 × 2.4 | 65 | 0.001431 | 6.04 | 8.000 | F, pL, mE 80° | WH I 157; h 150; GC 396; UGC 1256; MCG 4-5-11; CGCG 482-16; IRAS 01450+2710; VV 338; KCPG 40B |
| NGC 684 | 01 50 14.1 | +27 38 46 | Gx (Sb) | 13.3 | 12.4 | 0.9 | 12.8 | 3.2 × 0.6 | 87 | 0.011791 | 49.80 | 42.430 | F, vlE, * 13 f 100" | WH II 612; h 152; GC 403; IC 165; UGC 1292; MCG 4-5-17; CGCG 482-22; IRAS 01474+2724 |
| IC 1727 | 01 47 30.0 | +27 19 57 | Gx (SBm) | 12.1 | 11.5 | 0.6 | 14.7 | 5.7 × 2.4 | 150 | 0.001151 | 4.86 | 6.820 | F, L, st inv, I 157 nf | UGC 1249; MCG 4-5-9; CGCG 482-14; VV 338; KCPG 40A |
| IC 1731 | 01 50 12.5 | +27 11 46 | Gx (SBc) | 14.0 | 13.3 | 0.7 | 13.6 | 1.5 × 1 | 140 | 0.011685 | 49.36 | 42.320 | F, E npsf, bM, prob spir | UGC 1291; MCG 4-5-18; CGCG 482-21 |

Collinder 21
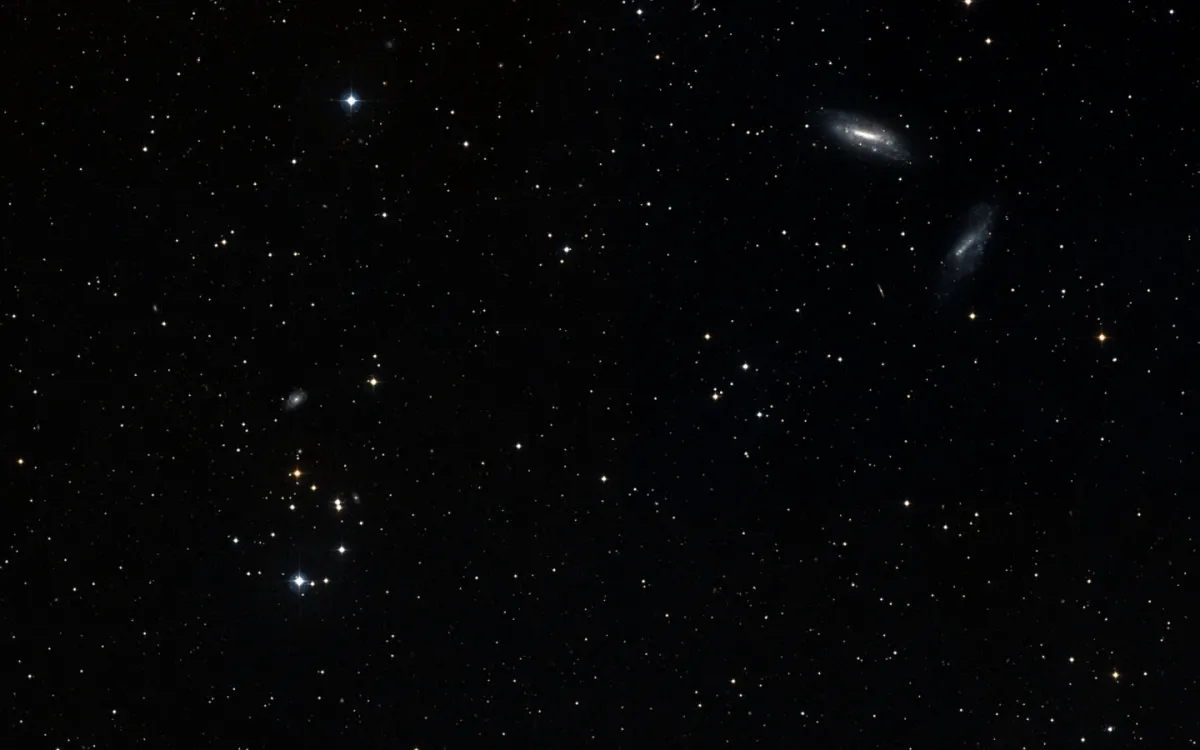
This cluster of stars with the conspicious "D" shape was discovered in 1931 by the Swedish Astronomer Per Collinder. He counted 12-15 stars and noted: «A small cluster cluster of bright stars, irregular. Cluster probability calculated according to Michell's (255) method = 27:1 This expresses the probability that the grouping is not accidental.» [455]
A later study of Collinder 21 showed random radial velocities and angular proper motions of the stars, which is evidence that these stars do not share a common mean tangential motions. Spectroscopic analysis revealed that five stars are giants and all the others are dwarfs. Distance ranges from 60 to 1470 parsec. The distance spread is to large to be a physical aggregate. The analysis showed that Collinder 21 is also not a remnant of an open cluster. [572]
The distance is estimated to 1400 pc. [145]
| Name | Collinder 21 |
| Object Type | Cluster of Stars |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 01h 50m 10s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +27° 06' 54" |
| Magnitudes | V 8.2 |
| Identifiers | C 0147+270; Cl Collinder 21; OCl 371; [KPS2012] MWSC 0143 |
Finder Chart
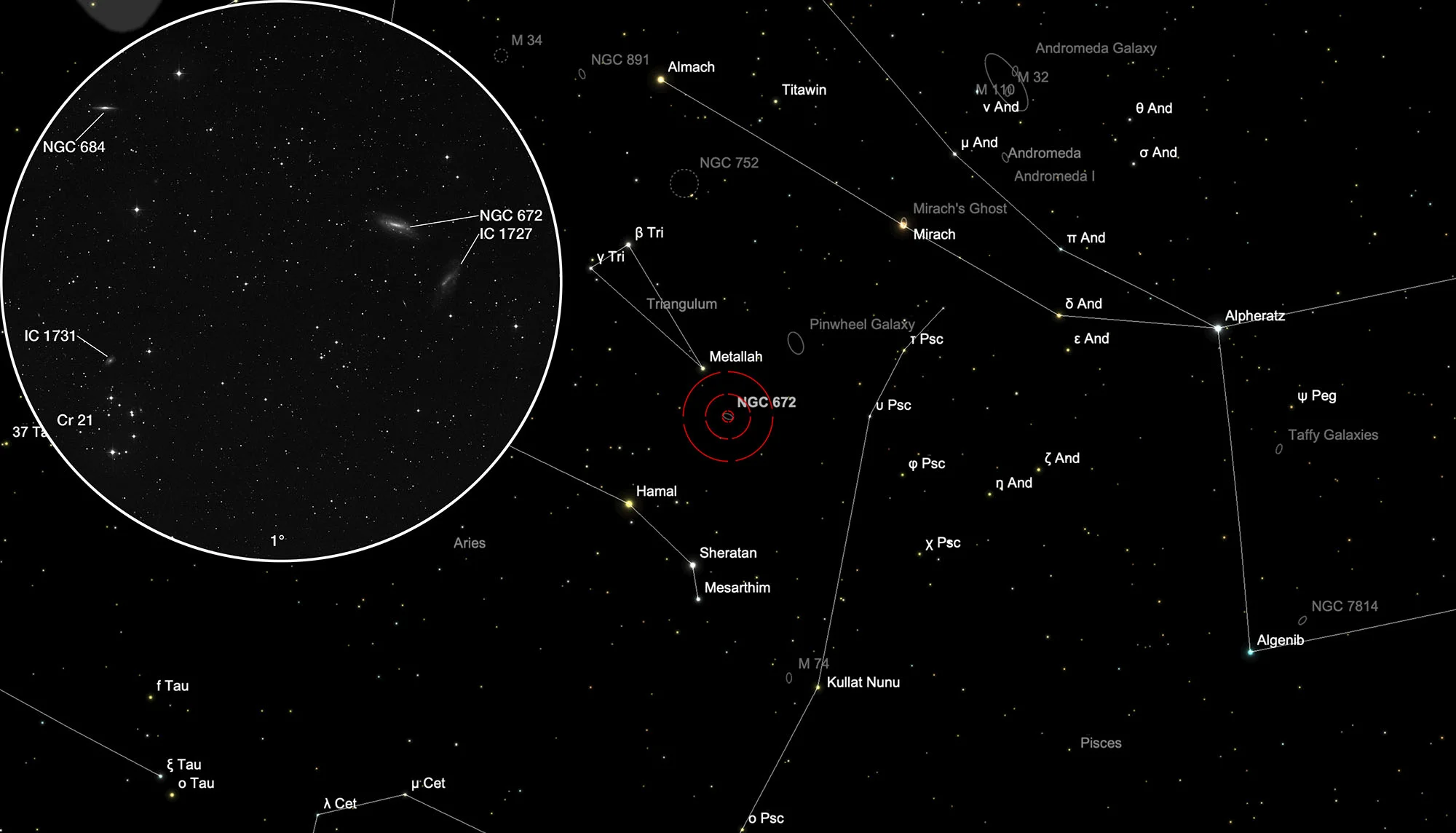
The galaxy pair NGC 672 + IC 1727 is located in the constellation Triangulum, about 40 arc minutes northwest of the small open star cluster Collinder 21. On 23 October it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is June to March.