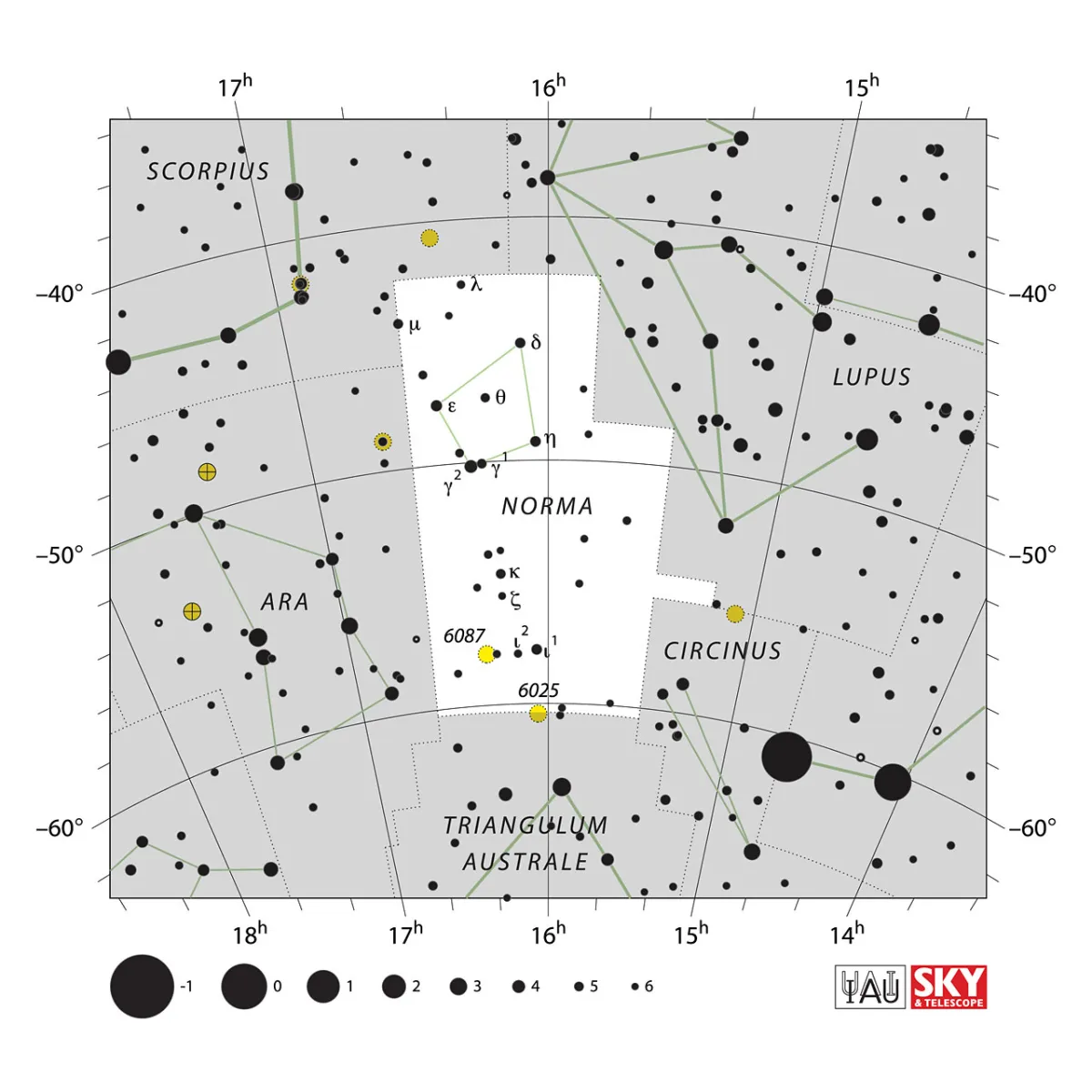
Constellation Norma (Carpenter's Square)
Properties
The constellation lies in the band of the Milky Way. A strip of galactic dust crosses the constellation from the north and divides the Milky Way into two halves, which reunite further to the southwest. Otherwise, Norma is a very inconspicuous constellation with stars just under 5th mag. The area is 165 square degrees and the centre culminates around midnight on May 21, and is not visible from Central Europe. [9, 15]
| IAU Name | Norma |
| IAU Genitive | Normae |
| IAU Abbr. | Nor |
| English Name | Carpenter's Square |
| Culmination at local midnight | 24 May |
| Season (Latitude +0.0°) | January … October |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 15h 12m 14s … 16h 36m 08s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -60° 26' 08" … -42° 16' 03" |
| Area | 165 deg2 |
| Neighbours (N↻) | Sco, Lup, Cir, TrA, Ara |
Deep-Sky Object Descriptions
Catalogues
History
Norma is a superfluous constellation from the series of technical and scientific devices by the unimaginative Frenchman Lacaille. It was introduced in 1752. Originally the stars belonged to the neighboring figures Ara and Lupus. The constellation boundaries proposed by Lacaille were changed afterwards, so that the stars α and β Normae no longer belong to them today. [7, 21]