Constellation Triangulum Australe (Southern Triangle)
Properties
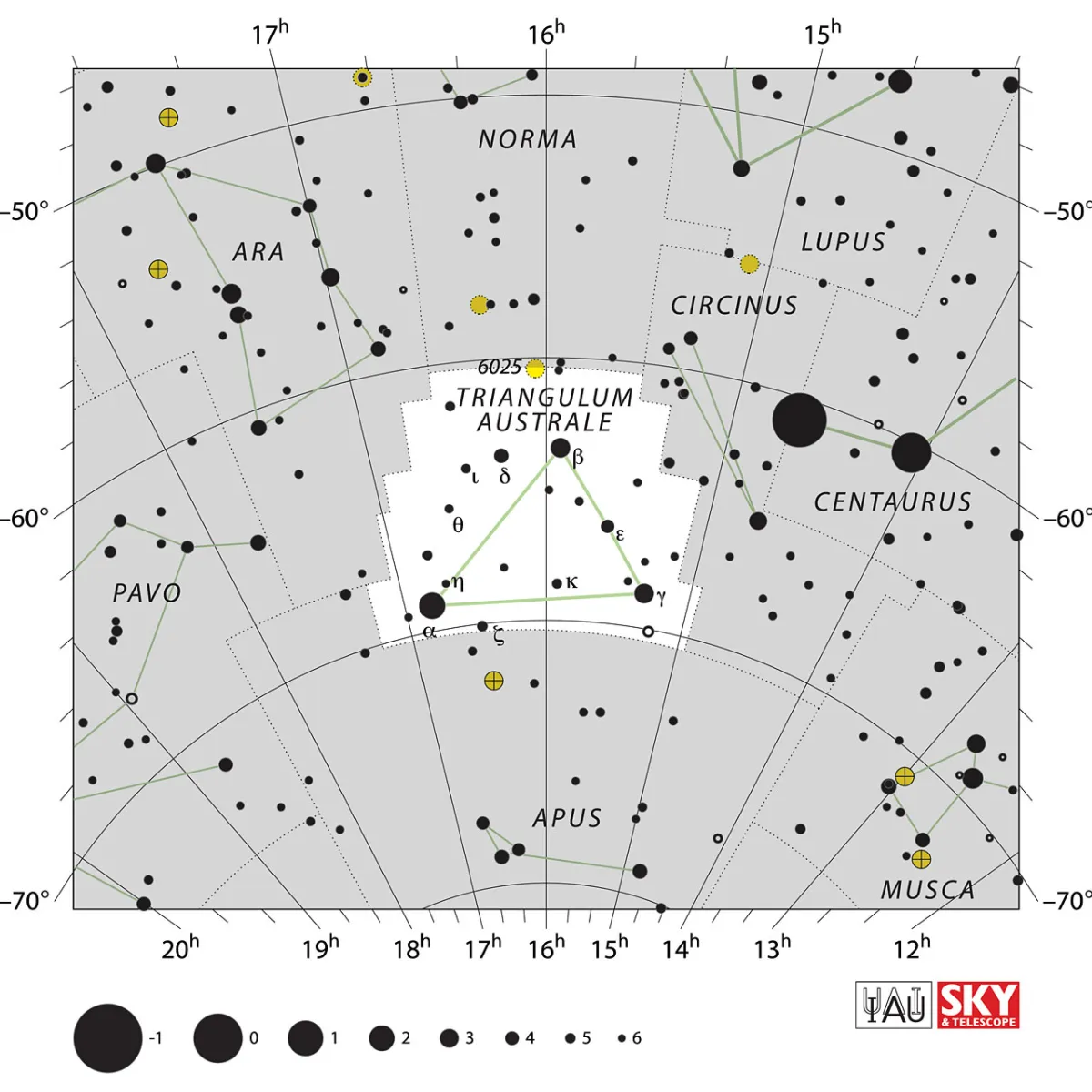
The constellation is small but noticeable at 110 square degrees, because the equilateral triangle is formed by three stars of the 2nd and 3rd magnitude. It is to the east of the two front cataracts of the Centaurs. The centre of the constellation culminates around midnight on May 22nd. [9, 15]
| IAU Name | Triangulum Australe |
| IAU Genitive | Trianguli Australis |
| IAU Abbr. | TrA |
| English Name | Southern Triangle |
| Culmination at local midnight | 24 May |
| Season (Latitude +0.0°) | January … October |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 14h 56m 01s … 17h 13m 53s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -70° 30' 42" … -60° 15' 52" |
| Area | 110 deg2 |
| Neighbours (N↻) | Nor, Cir, Aps, Ara |
Deep-Sky Object Descriptions
Catalogues
History
The constellation was introduced in 1603 by Johann Bayer as a southern counterpart to the long-known triangulum in his Uranometria. It was proposed by Pieter Theodor a century earlier. [7]