Hercules Galaxy Cluster (ACO 2151)

History
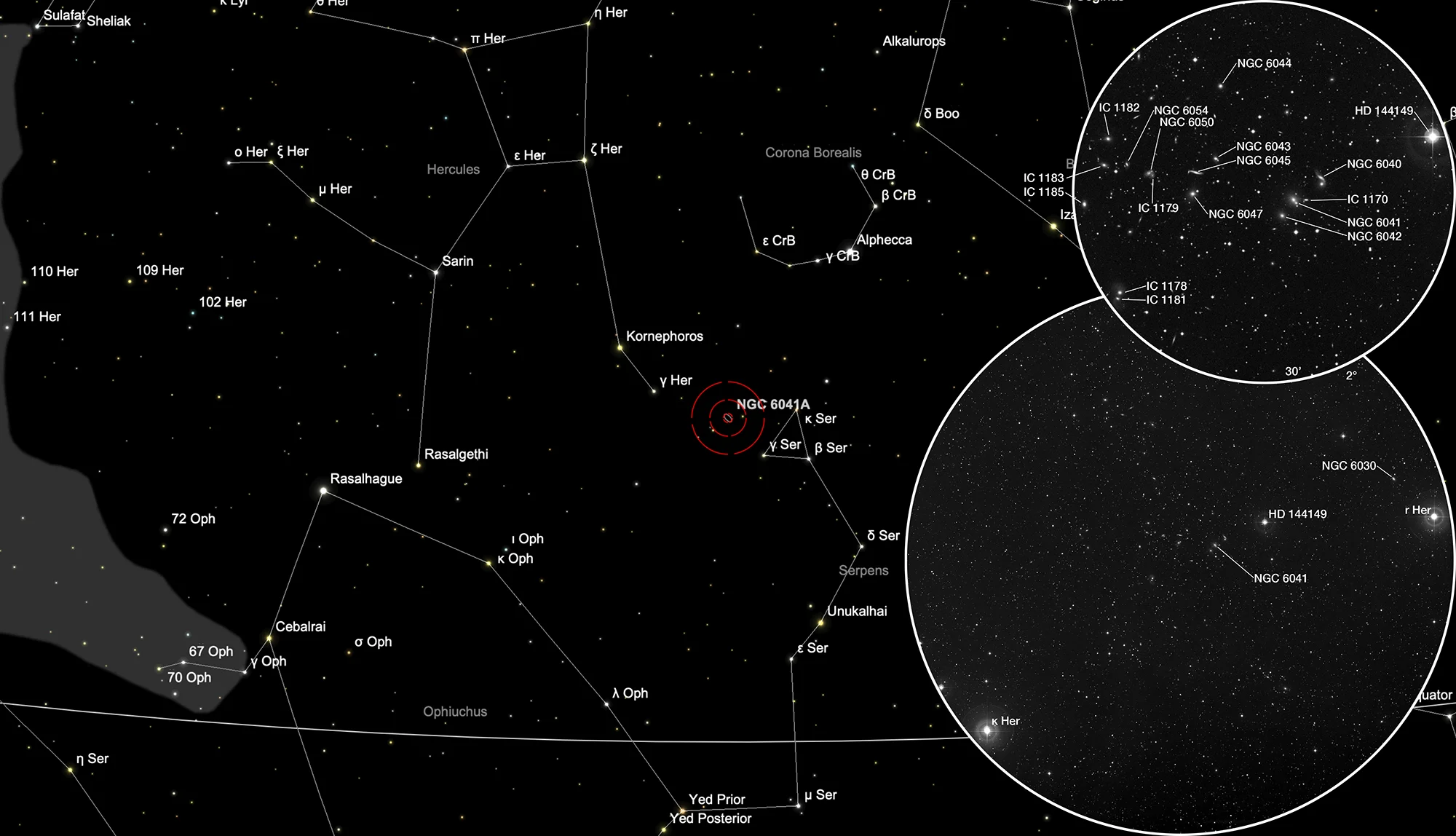
The first member galaxies (NGC 6040, NGC 6041 and NGC 6042) had been discovered on 4 June 1869 by French astronomer Édouard Stephan using the the 31-inch Foucault reflector at Marseille observatory. [277]
From 6 to 27 June 1886 American astronomer Lewis Swift observed this part of the sky with the 16-inch Refractor at Warner Observatory, Rochester and ten more members of this galaxy cluster: NGC 6039, NGC 6043, NGC 6044, NGC 6045, NGC 6047, NGC 6050, NGC 6055, NGC 6056, NGC 6057 and NGC 6061. [277] NGC 6039 is a duplicate entry of NGC 6042: Swift decribed it as «eeeF, vS, R; sp. of 3 in a line; the other 2 being 2 of Stephan's; 3rd of 10». [679] The «sp» (south-preceding) in his description is most likely a typing error and should read «sf» (south-following). Then the description «south-following of 3 in a line» matches for NGC 6042, being the other two NGC 6040 and NGC 6041. [196, 204]
Between 1888 and 1892 Swift, Javelle and Bigourdan discovered further nebulae which were later added to Dreyer's «Index Catalogue». [314]
The Hercules Galaxy Cluster was first described by Harlow Shapley in 1933. [673] In 1958 George Ogden Abell published his catalogue «The Distribution of Rich Clusters of Galaxies» which contains 2712 clusters identified on the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS) photo plates. This cluster was listed with the number 2151 and mostly is identified as A 2151 or Abell 2151. [674] In 1989 this catalog was extended by Harold G. Corwin Jr. and Ronald P. Olowin with clusters of the southern hemisphere to total 4073 galaxy clusters. [675] To prevent identification confusion with Abell planetary nebulae, the galaxy cluster should be identified as ACO 2151, where ACO stands for Abell, Corvin, Olowin. [145]
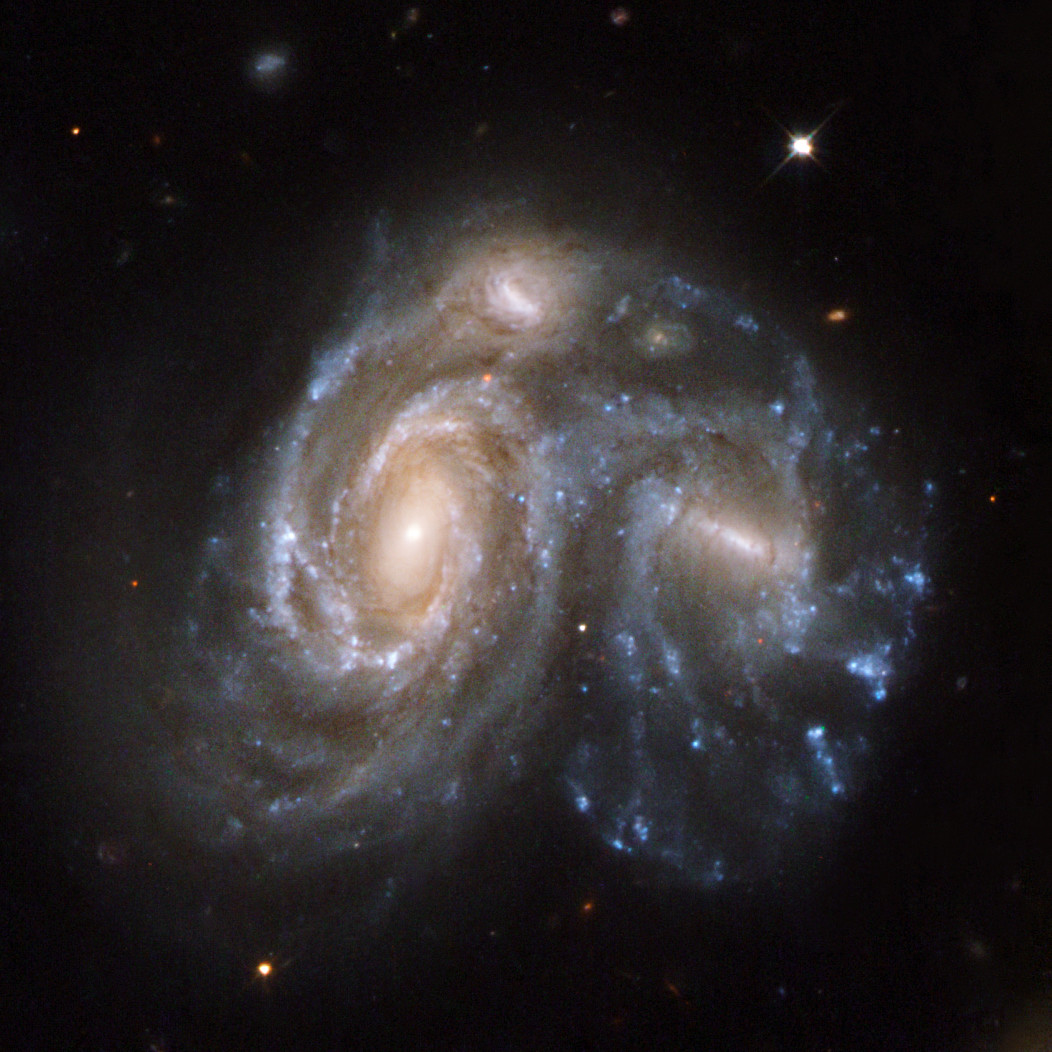
Halton Arp divided his «Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies», published in 1966, into groups based on purely morphological criteria. From Hercules Galaxy Cluster he added four examples: Arp 71 (NGC 6045), Arp 122 (NGC 6040 + LEDA 59642), Arp 172 (IC 1178, IC 1181), Arp 272 (NGC 6050 + IC 1179). [199]



Physical Properties
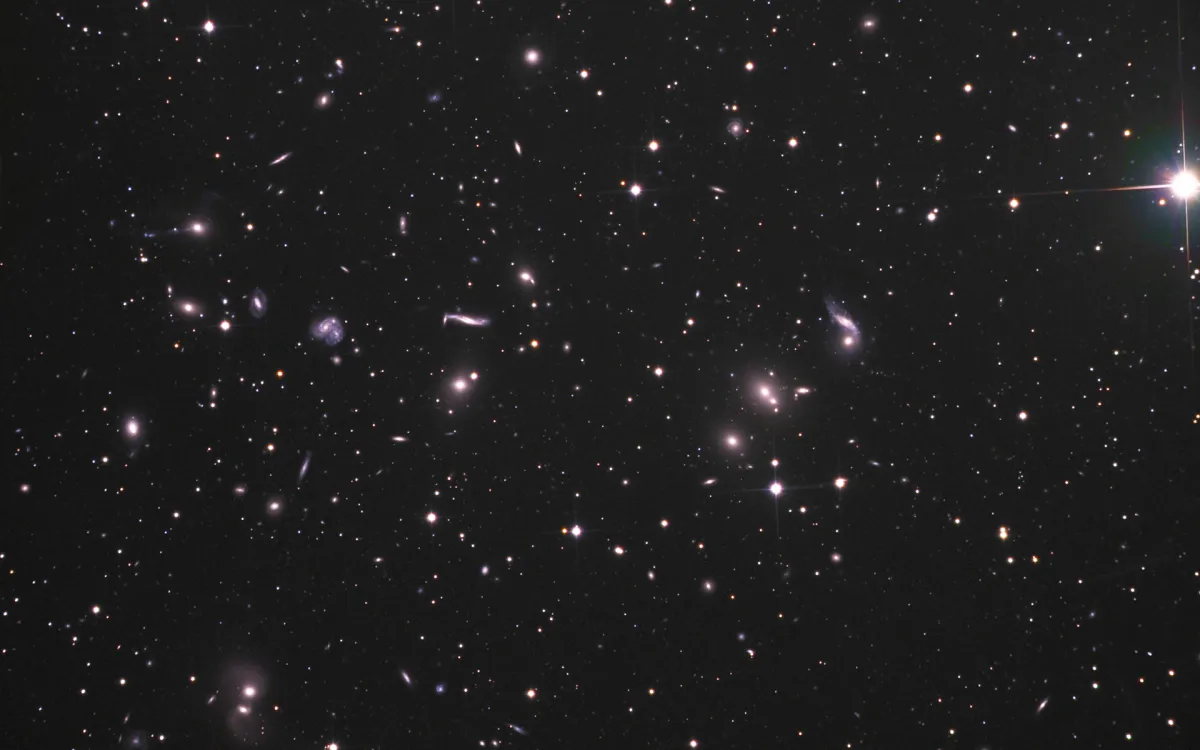
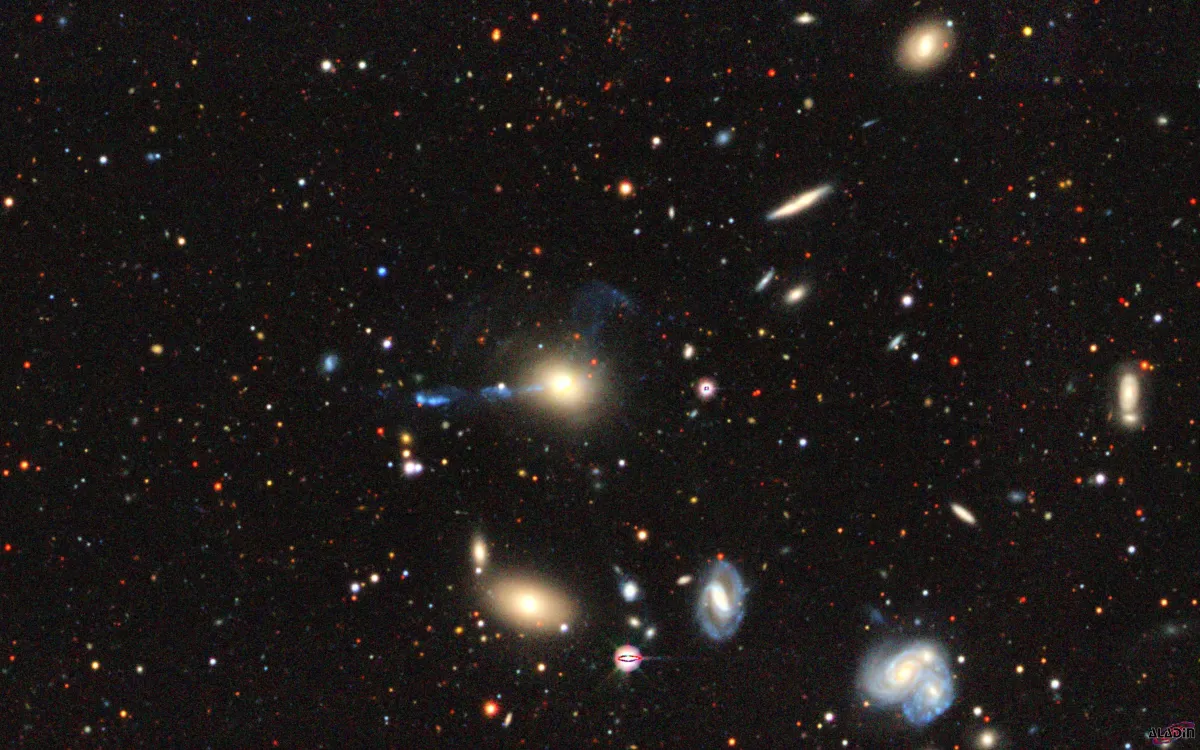
The Hercules Galaxy Cluster contains more than 100 members, and spans about 1° section of the sky. Medium distance is about 156 Mpc and it is part of the larger Hercules Supercluster, whic itself belongs to the much larger Great Wall super-structure. Shown below are data of just the brightes members in the 30 arcmin closeup in the finder chart. For more details about the galaxy cluster, see ACO 2151 at CDS.
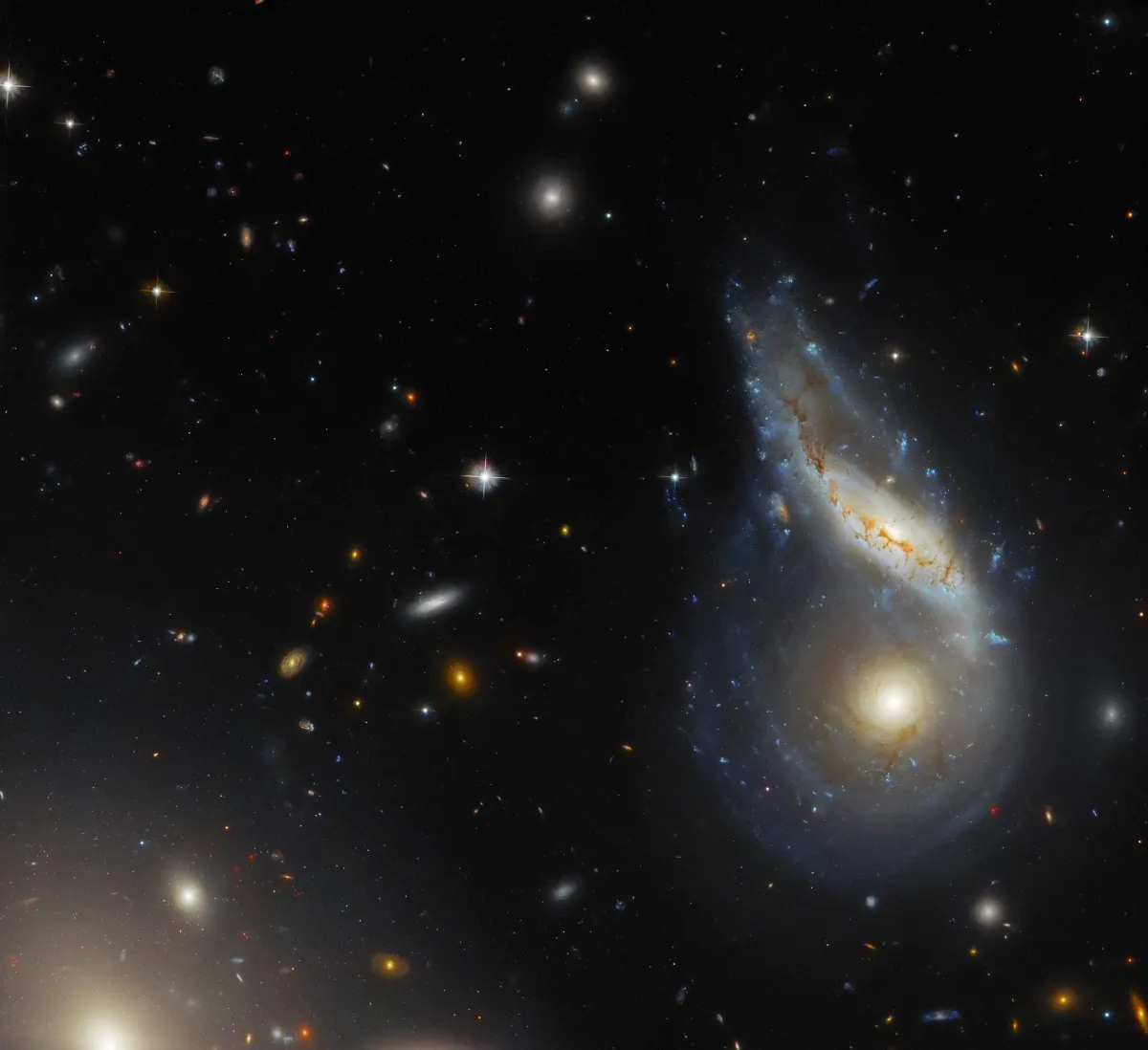
Noteworthy among the galaxies in the Hercules Galaxy Cluster is the galaxy IC 1182, which displays a striking jet extending eastward from its core. This jet consists of a chain of energetic knots propelled outward from the center. On the opposite side lies a broad but fainter S-shaped plume, accompanied by additional surrounding debris. The central region of IC 1182 contains intensely emitting gas and numerous clusters of hot, blue stars. Together, these features highlight the galaxy’s highly active nature: it emits large amounts of energy and expels significant quantities of material into the surrounding space at high velocities. Several explanations have been proposed for this activity, but the most likely is a collision between two galaxies. [747]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 6039 | 16 04 39.5 | +17 42 01 | dup | 14.9 | 14.0 | 0.9 | 13.3 | 0.8 × 0.7 | 65 | 0.034874 | 147.3 | eeF, vS, R, sp of 3 in line | NGC 6042; MCG 3-41-79; CGCG 108-104; DRCG 34-63 | |
| NGC 6040 A | 16 04 26.7 | +17 45 00 | Gx (SBc) | 15.1 | 14.2 | 0.9 | 13.6 | 1.3 × 0.7 | 42 | 0.042079 | 177.7 | vF, eS, F * close | GC 5799; UGC 10165; MCG 3-41-74; CGCG 108-96; Arp 122; VV 212; DRCG 34-67 | |
| NGC 6040 B | 16 04 26.5 | +17 44 31 | Gx (S0) | 14.9 | 14.0 | 0.9 | 13.4 | 0.8 × 0.8 | 0.040935 | 172.9 | vF, eS, F * close | GC 5799; UGC 10165; MCG 3-41-73; CGCG 108-96; Arp 122; VV 212; DRCG 34-68 | ||
| NGC 6041 A | 16 04 35.8 | +17 43 17 | Gx (E-S0) | 14.4 | 13.3 | 1.1 | 13.5 | 1.3 × 1.1 | 36 | 0.035151 | 148.4 | F, S | GC 5800; UGC 10170; MCG 3-41-78; CGCG 108-101; VV 213; DRCG 34-64 | |
| NGC 6041 B | 16 04 35.0 | +17 43 02 | Gx (E-S0) | 16.6 | 15.6 | 1.0 | 13.4 | 0.4 × 0.3 | 88 | 0.034777 | 146.9 | F, S | GC 5800; UGC 10170; MCG 3-41-78; CGCG 108-101; VV 213; DRCG 34-65 | |
| NGC 6042 | 16 04 39.5 | +17 42 01 | Gx (E-S0) | 14.9 | 14.0 | 0.9 | 13.3 | 0.8 × 0.7 | 65 | 0.034874 | 147.3 | vF, vS | GC 5801; NGC 6039; MCG 3-41-79; CGCG 108-104; DRCG 34-63 | |
| NGC 6043 A | 16 05 01.5 | +17 46 33 | Gx (SB0) | 15.3 | 14.3 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 0.7 × 0.4 | 55 | 0.033039 | 139.5 | eeF, pS, lE, "4th of 10" | MCG 3-41-86; CGCG 108-109; DRCG 34-83 | |
| NGC 6043 B | 16 05 00.7 | +17 46 24 | Gx (C) | 16.2 | 15.2 | 1.0 | 12.4 | 0.3 × 0.3 | 0.030981 | 130.8 | eeF, pS, lE, "4th of 10" | MCG 3-41-86; CGCG 108-109 | ||
| NGC 6044 | 16 04 59.6 | +17 52 13 | Gx (S0) | 15.3 | 14.3 | 1.0 | 13.0 | 0.6 × 0.6 | 0.033106 | 139.8 | eeF, vS, R, vF * close p | IC 1172; MCG 3-41-84; CGCG 108-110; DRCG 34-93 | ||
| NGC 6045 A | 16 05 08.0 | +17 45 29 | Gx (SBc) | 14.9 | 13.9 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 1.3 × 0.3 | 82 | 0.033310 | 140.7 | 145.50 | eeF, vS, R, v diffic | UGC 10177; MCG 3-41-88; CGCG 108-112; DRCG 34-82; Arp 71; IRAS 16028+1753 |
| NGC 6045 B | 16 05 10.3 | +17 45 30 | Gx (S0) | 16.5 | 15.5 | 1.0 | 12.6 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 160 | 0.031184 | 131.7 | eeF, vS, R, v diffic | DRCG 34-81 | |
| NGC 6047 | 16 05 09.0 | +17 43 47 | Gx (E3) | 14.6 | 13.5 | 1.1 | 13.4 | 1.1 × 0.8 | 90 | 0.031262 | 132.0 | 112.00 | eF, R, pS, F * close n | MCG 3-41-87; CGCG 108-111; DRCG 34-62 |
| NGC 6050 A | 16 05 23.5 | +17 45 26 | Gx (SBc) | 15.4 | 14.7 | 0.7 | 13.9 | 0.9 × 0.6 | 132 | 0.031928 | 134.8 | 151.50 | eeF, S, R, v diffic | IC 1179A; UGC 10186; MCG 3-41-93; DRCG 34-156; CGCG 108-118; Arp 272; VV 220; KCPG 481B |
| NGC 6050 B | 16 05 22.3 | +17 45 16 | Gx (SBc) | 16.0 | 15.4 | 0.6 | 13.7 | 0.4 × 0.3 | 35 | 0.037116 | 156.7 | eeF, S, R, v diffic | IC 1179B; UGC 10186; MCG 3-41-92; DRCG 34-155; CGCG 108-118; Arp 272; VV 220; KCPG 481A | |
| NGC 6054 | 16 05 38.1 | +17 46 03 | Gx (SB0) | 15.3 | 14.2 | 1.1 | 12.9 | 0.8 × 0.4 | 65 | 0.034010 | 143.6 | eeF, pS, lE, F * sp | IC 1183; MCG 3-41-103; CGCG 108-128; DRCG 34-77 | |
| IC 1170 | 16 04 31.6 | +17 43 17 | Gx (E-S0) | 15.9 | 14.9 | 1.0 | 12.2 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 88 | 0.032166 | 135.8 | vF, vS, vSFN, 6041 f | CGCG 108-101; DRCG 34-66 | |
| IC 1178 | 16 05 33.0 | +17 36 07 | Gx (E-S0) | 15.2 | 14.1 | 1.1 | 13.9 | 1 × 0.9 | 36 | 0.033687 | 142.2 | eeF, pS, bet 2 st | UGC 10188; MCG 3-41-97; CGCG 108-120; DRCG 34-40; Arp 172; VV 194; NPM1G +17.0583 | |
| IC 1179 A | 16 05 23.5 | +17 45 26 | dup | 15.4 | 14.7 | 0.7 | 13.9 | 0.9 × 0.6 | 132 | 0.031928 | 134.8 | 151.50 | eeF, pS, R [? 6054] | NGC 6050A; UGC 10186; MCG 3-41-93; DRCG 34-156; CGCG 108-118; Arp 272; KCPG 481B; VV 220 |
| IC 1179 B | 16 05 22.3 | +17 45 16 | dup | 16.0 | 15.4 | 0.6 | 13.7 | 0.4 × 0.3 | 35 | 0.037116 | 156.7 | eeF, pS, R [? 6054] | NGC 6050B; UGC 10186; MCG 3-41-92; DRCG 34-155; CGCG 108-118; Arp 272; KCPG 481A; VV 220 | |
| IC 1181 | 16 05 33.9 | +17 35 37 | Gx (SB0-a) | 15.9 | 14.8 | 1.1 | 14.0 | 0.8 × 0.4 | 70 | 0.033066 | 139.6 | eeF, S, R, ‘ 12th of 12 ’ | UGC 10189; MCG 3-41-98; CGCG 108-120; VV 194; Arp 172; DRCG 34-39 | |
| IC 1182 | 16 05 36.7 | +17 48 10 | Gx (S0-a) | 15.2 | 14.2 | 1.0 | 12.9 | 1 × 0.5 | 81 | 0.034157 | 144.2 | 163.00 | vF, S, dif, lbM | UGC 10192; MCG 3-41-104; CGCG 108-126; DRCG 34-78; KUG 1603+179B; NPM1G +17.0584; MK 298 |
| IC 1183 | 16 05 38.1 | +17 46 03 | dup | 15.3 | 14.2 | 1.1 | 12.9 | 0.8 × 0.4 | 65 | 0.034010 | 143.6 | vF, vS, stellar, * 11 sp 1' | NGC 6054; MCG 3-41-103; CGCG 108-128; DRCG 34-77 | |
| IC 1185 | 16 05 44.6 | +17 43 02 | Gx (Sab) | 14.9 | 13.9 | 1.0 | 12.7 | 0.8 × 0.5 | 0 | 0.034764 | 146.8 | * 13 with S neb | MCG 3-41-110; CGCG 108-134; NPM1G +17.0585; DRCG 34-59 |
Finder Chart
The Hercules Galaxy Cluster Abell 2151 is located in the constellation Hercules, right beside the head of Serpens. Point your telescope with the widest field of view between the 5.1 mag star r Herculii and binary star κ Herculii (5.0 mag and 6.2 mag, 27" separation). The centre of the cluster lies west of the 6.7 mag star HD 144149 and roughly stretches in north-south direction. The galaxy cluster is in opposition to the sun on 25 May and can best be observed in the months of January to November.
Visual Observation
320 mm Aperture: The Hercules galaxy cluster Abell 2151 offered 9 galaxies. Parallel to the three stars arranged at right angles were the two double pairs NGC 6040 A+B and NGC 6041 A+B, along with IC1170, which is located to the left of the latter pair of galaxies, and NGC 6042. The IC 1170 is extremely faint and can only be glimpsed indirectly. Among the double pairs, NGC 6040 A+B is the most difficult pair. The three galaxies NGC 6043, NGC 6045, and NGC 6047 are located below a very wide double star pair. — 12.5" Ninja-Dobson F:4.5 / TV-Radian 8 mm, 181x, 0.33°, Glaubenberg, 7. 7. 2002, Eduard von Bergen