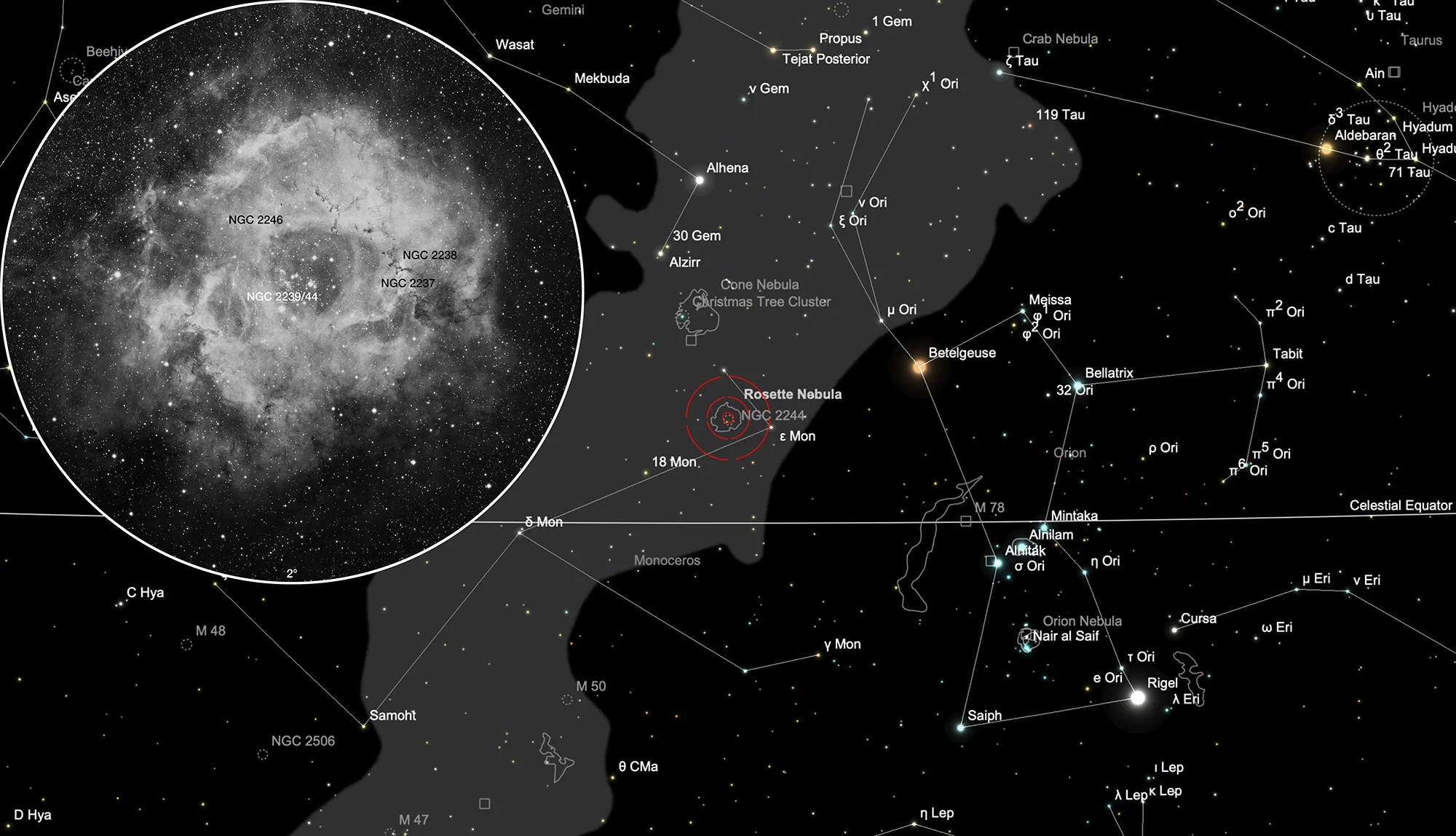
Rosette Nebula (NGC 2237+)
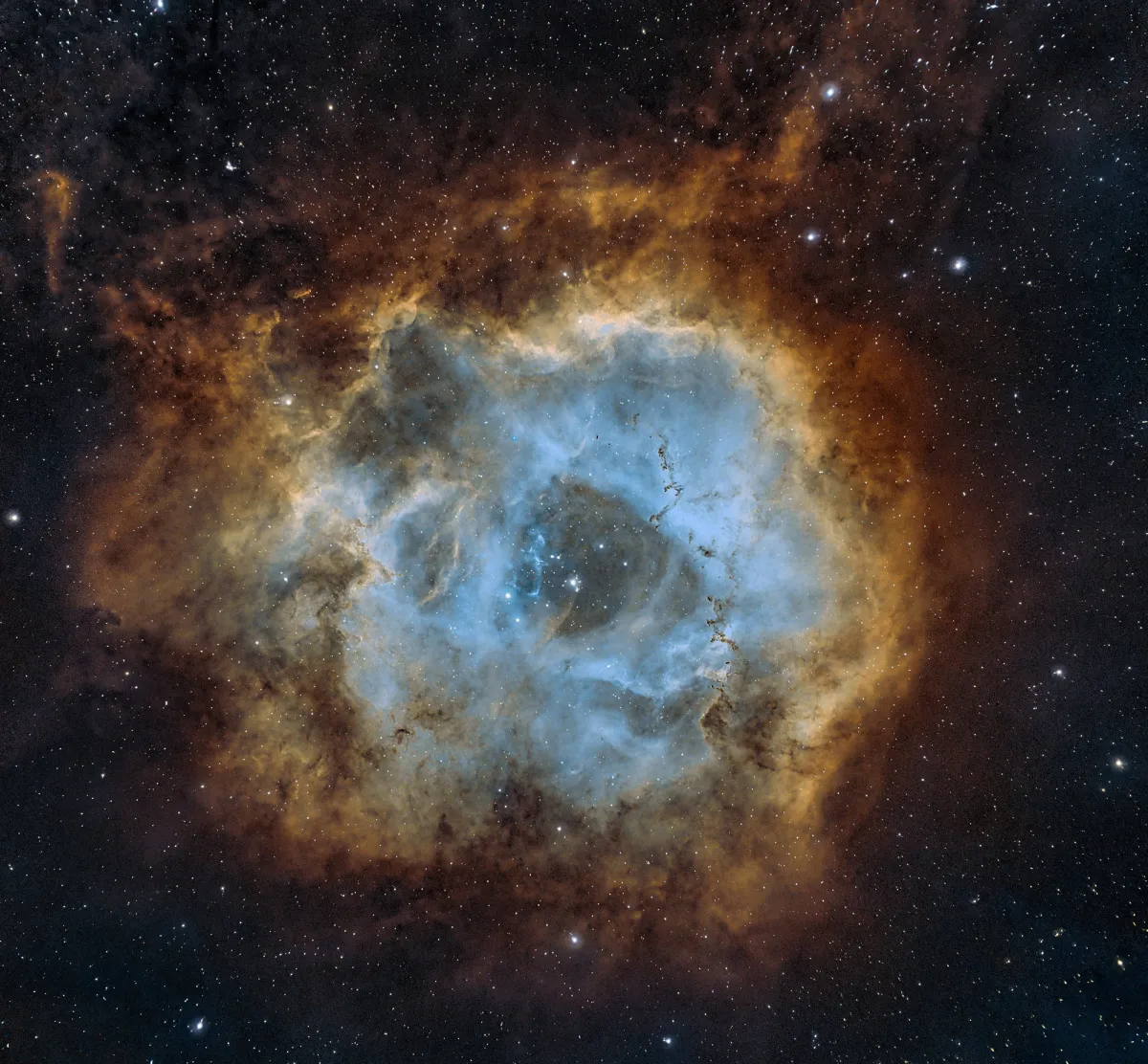
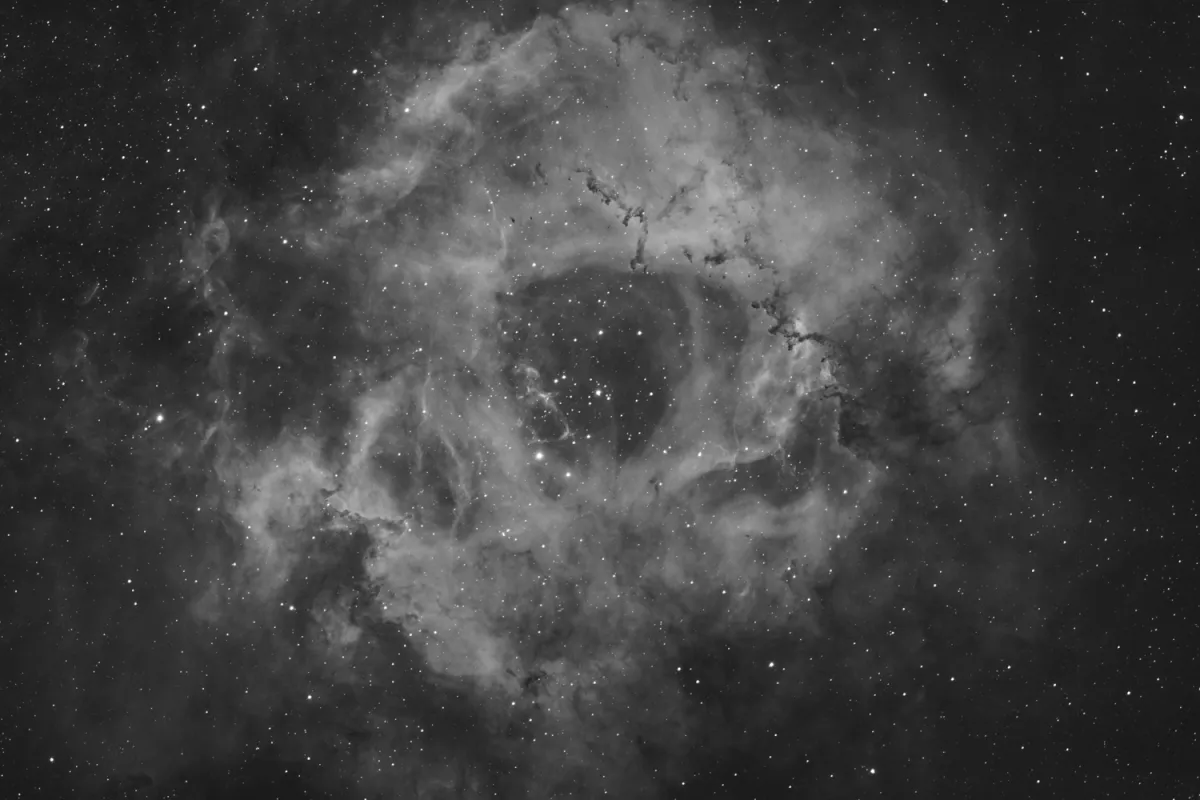
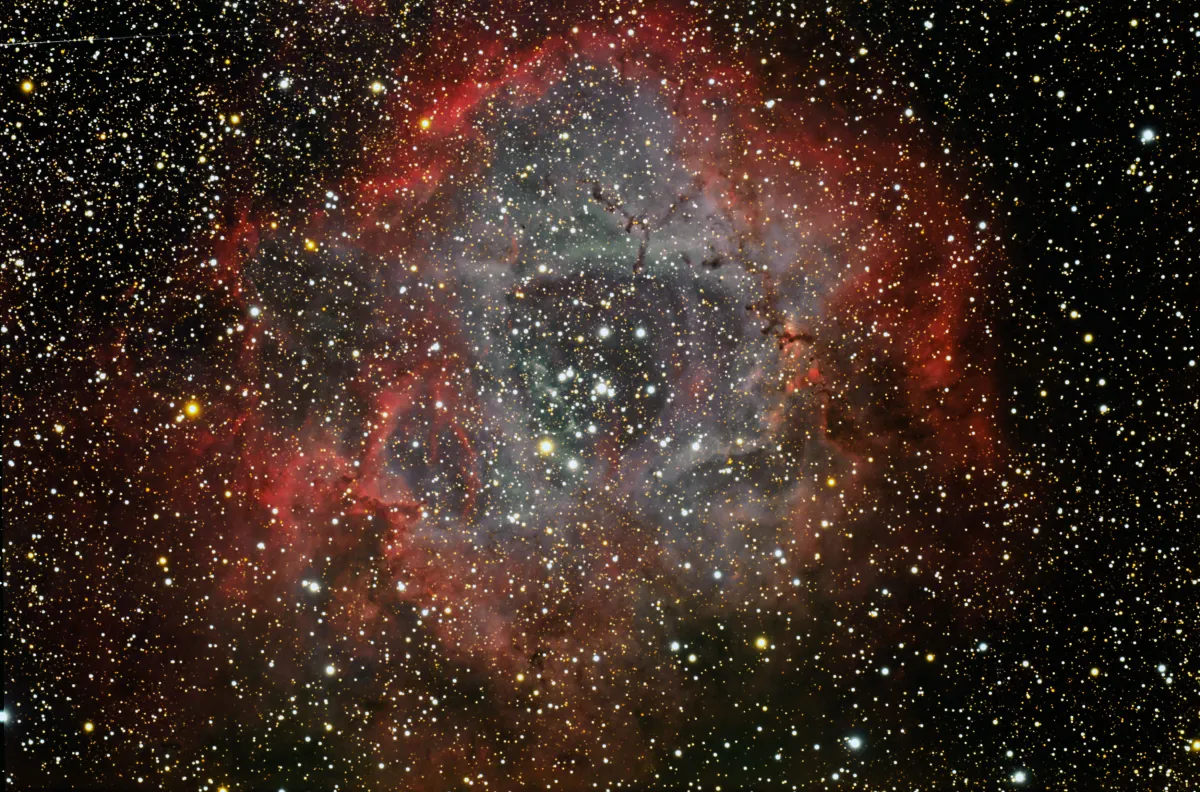
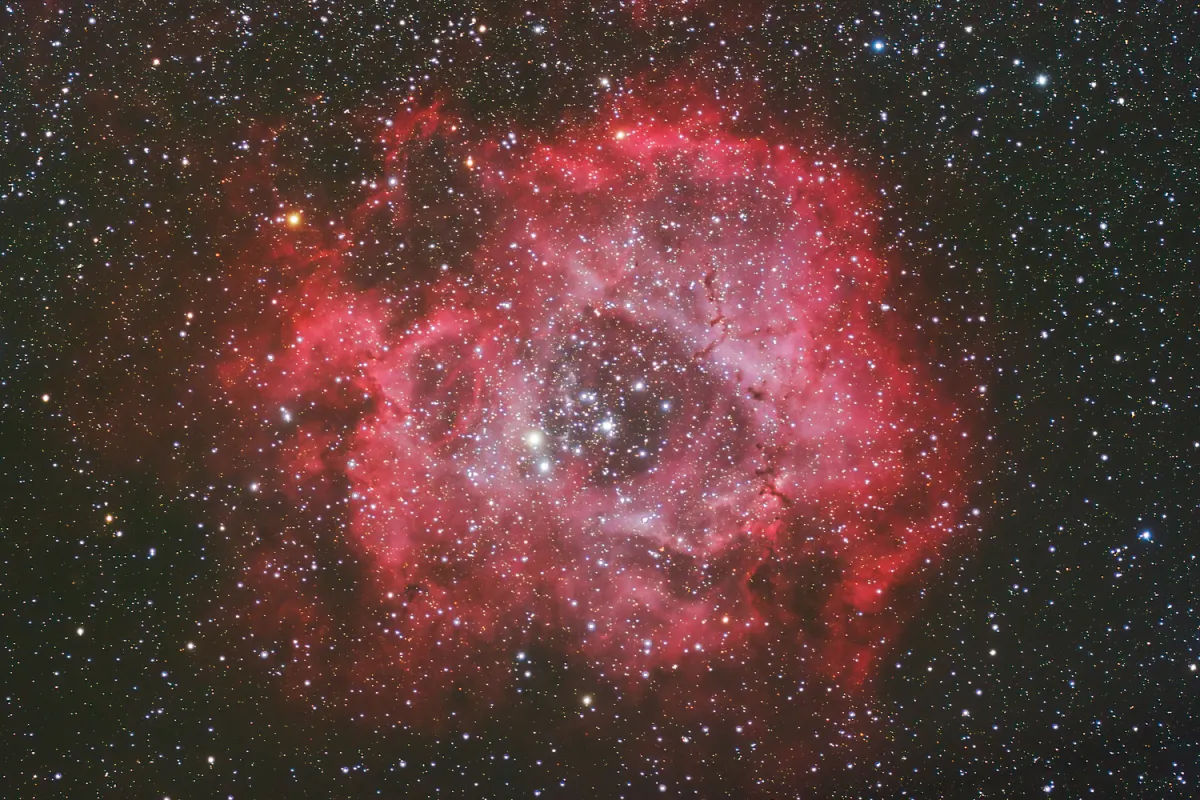





History
The open star cluster in the Rosette Nebula was first recorded by British astronomer John Flamsteed on 17 February 1690. [277] William Herschel cataloged it on 24 January 1784 as VII 2, with the class VII representing «pretty much compressed clusters of large or small stars». He described it as follows: «A beautiful cluster of scattered stars chiefly of 2 sorts. The first large, the second arranged in winding lines. Contains the 12th Monoc.» [463] That star cluster was later listed as NGC 2244 in Dreyers «New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars». [313]
On 4 March 1830 Herschel's son John, rediscovered the same star cluster and cataloged it as h 392 (GC 1420) and described it as «stars of 8th magnitude in large pretty bright cluster» [467]. His discovery was later given the number NGC 2239 by Dreyer. [313]
On 28 February 1864 the German astronomer Albert Marth discovered «small stars in nebulosity». He was observing in Malta, using William Lassell's 48 inch reflector. His discovery was later added as GC 5361 by John Herschel and then as NGC 2238 by Dreyer. [142, 313]
The American astronomer Lewis Swift was using the 16 inch refractor at Warner Observatory in 1865 and noticed a «pretty bright, very very large diffuse» nebula around the star cluster. His discovery was cataloged by Dreyer as NGC 2237 with the remark that it may be the same as GC 5361 (NGC 2238). On 27 February 1886 Swift looked again at the same spot and noticed another «most extremely faint, large, irregular round, extremely difficult» nebula, which was then added as NGC 2246 by Dreyer. [196, 313]
The designation NGC 2239 is usually used for the Rosette Nebula, but this is not correct. Based on Dreyer's description, NGC 2239 is Herschel's star cluster and the designations related to the surrounding nebula are NGC 2237, NGC 2238 and NGC 2246.
Physical Properties
The Rosette Nebula is an H-II region, a star-forming region with clouds of gas and dust. At a distance of about 5000 to 5200 light-years and a diameter of 130 light-years, it appears relatively large in the sky, about 80 x 60 arc minutes. The mass of the nebula is estimated at around 10'000 solar masses. [196]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | Dim | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 2237 | 06 30 54.6 | +05 02 52 | EN | 80 × 50 | 1.600 | pB, vvL, dif (? = 5361) | w part of Rosette nebula | ||
| NGC 2238 | 06 30 40.3 | +05 00 47 | EN | 6.0 | 80 × 60 | 1.600 | S * in nebulosity | GC 5361; LBN 948; knot in Rosette nebula | |
| NGC 2239 | 06 32 19.0 | +04 51 24 | dup | 5.3 | 4.8 | 24 | 1.445 | * 8 in L, P, B Cl | h 392; GC 1420; NGC 2244; OCL 515; in Rosette nebula |
| NGC 2244 | 06 32 19.0 | +04 51 24 | OCL (II3p) | 5.3 | 4.8 | 24 | 1.445 | Cl, beautiful, st sc (12 Monoc) | WH VII 2; GC 1424; NGC 2239; OCL 515; in Rosette nebula |
| NGC 2246 | 06 32 33.7 | +05 07 42 | EN | 1.600 | eeF, L, irrR, e diffic | LBN 948; part of Rosette nebula |
Finder Chart
The open star cluster NGC 2239 with the Rosette Nebula around it is located in the constellation Monoceros, a rather inconspicuous constellation along with Orion in the Milky Way band. On clear, dark winter nights the star cluster NGC 2239 is visible to the naked eye, otherwise the two stars ε Monocerotis (4.4 mag) and 13 Monocerotis (4.51 mag) help position the Telrad.
Visual Observation
400 mm aperture: The huge nebula is about two times larger than the field of view of my 21 mm Ethos eyepiece (85x). Without filter only a grayish haze around the open cluster is detectable. With O-III filter the nebula pops out with high contrast and one can see structures in it. A fine sight. — Taurus T400 f/4.5 Dobsonian, Bernd Nies, Glaubenberg Langis, 28 February 2022