Planetary Nebula NGC 6891
History
This planetary nebula was discovered on 22 September 1884 by the Scottish astronomer Ralph Copeland using visual spectroscopy with a 6.1 inch refractor at Earl of Crawford's Observatory, Dun Echt, Aberdeen. [277]
Physical Properties
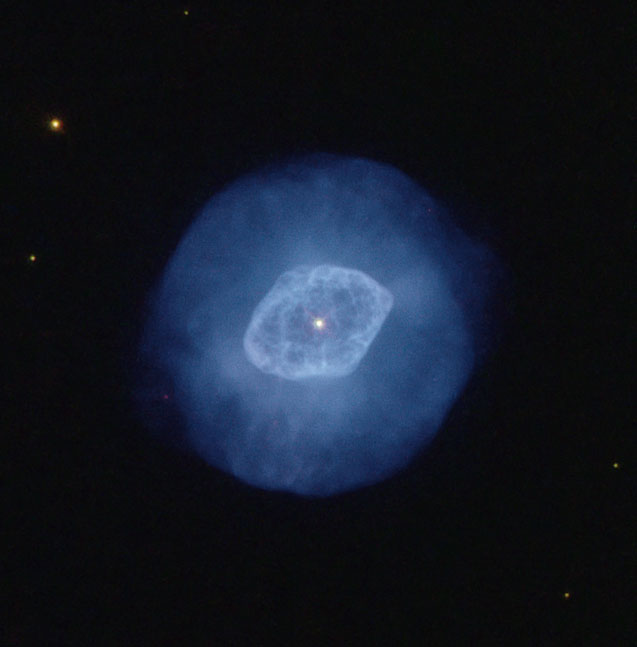
NGC 6891 is a triple-shell planetary nebula: It shows a bright central nebula which is surrounded by an attached shell and a detached outer halo. The inner and intermediate shells are ellipsoids with similar major to minor axial ratios, but different spatial orientations. The kinematical age of the intermediate shell is 4800 years and of the halo is 28'000 years. An outflow is observed to protrude from the tips of the major axis of the inner nebula and impact on the outer edge of the intermediate shell. The mass of the central white dwarf star is estimated to 0.75 times the mass of our Sun. Its surface temperature is 50'000 K. The distance to Earth is 3.8 kpc. [586]
| Designations | PN G054.1-12.1: NGC 6891, PK 54-12.1, ARO 37, VV 253, VV' 529 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 20h 15m 09s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +12° 42' 07" |
| Dimensions | 15." (optical) |
| Distance | 0.83 kpc |
| Radial Velocity | +42.4 ± 1.0 km/s |
| Expansion Velocity | 7.0 (O-III) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 403, BD +12 4266, EM* CDS 1140, GCRV 12622, HD 192563 |
| C-Star Magnitude | B: 12.30, V: 12.42 |
| C-Star Spectral Type | Of (H) |
| Discoverer | COPELAND 1884 |
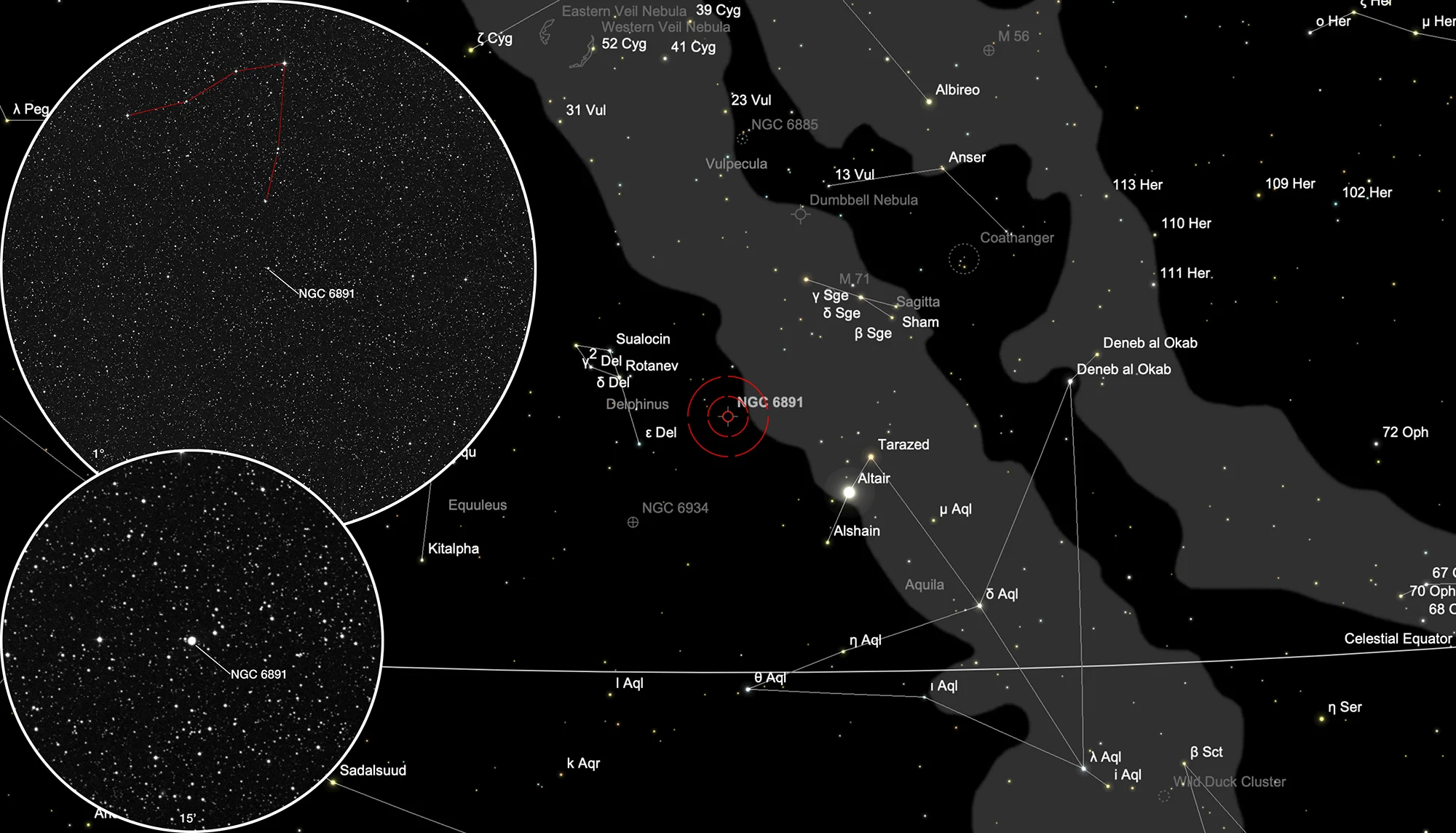
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula NGC 6891 is not easy to find, as it is located in a relatively star-poor area between Delphinus and Aquila befindet. On 25 July it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is from March to December.
Visual Observation
400 mm Aperture: In the 21 mm Tele Vue Ethos eyepiece, the figure shown in the 1° close-up doesn't immediately catch one's eye, and locating it isn't quite easy. With some patience and multiple repositioning of the Telrad, it is possible to eventually find the small, slightly bluish round speck. In the 9 mm Nagler eyepiece, the planetary nebula becomes somewhat clearer, and a central star can be discerned. However, it was not possible to observe that the inner part should be brighter. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Glaubenberg, 11. 10. 2023, SQM 20.9, Bernd Nies