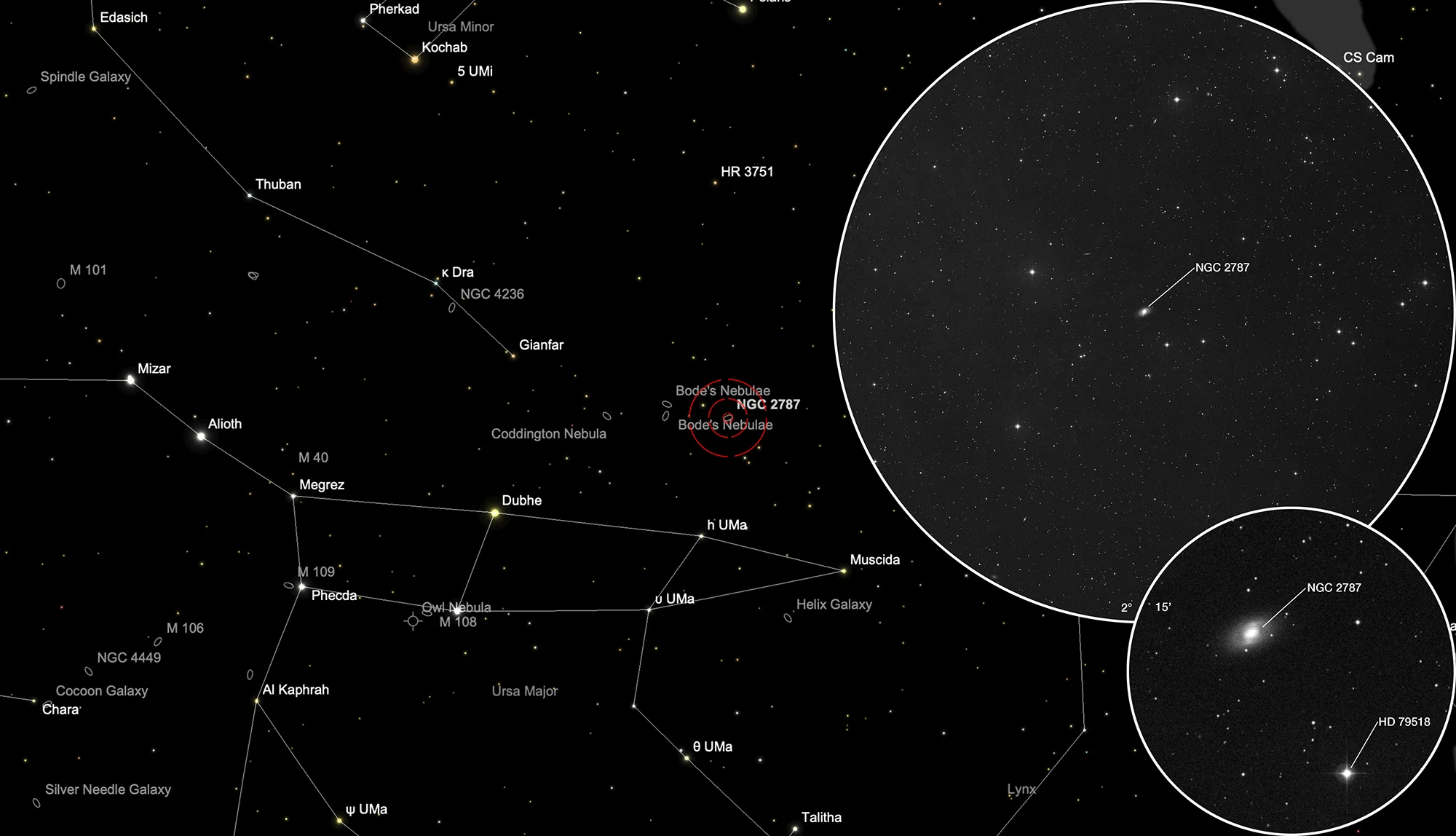
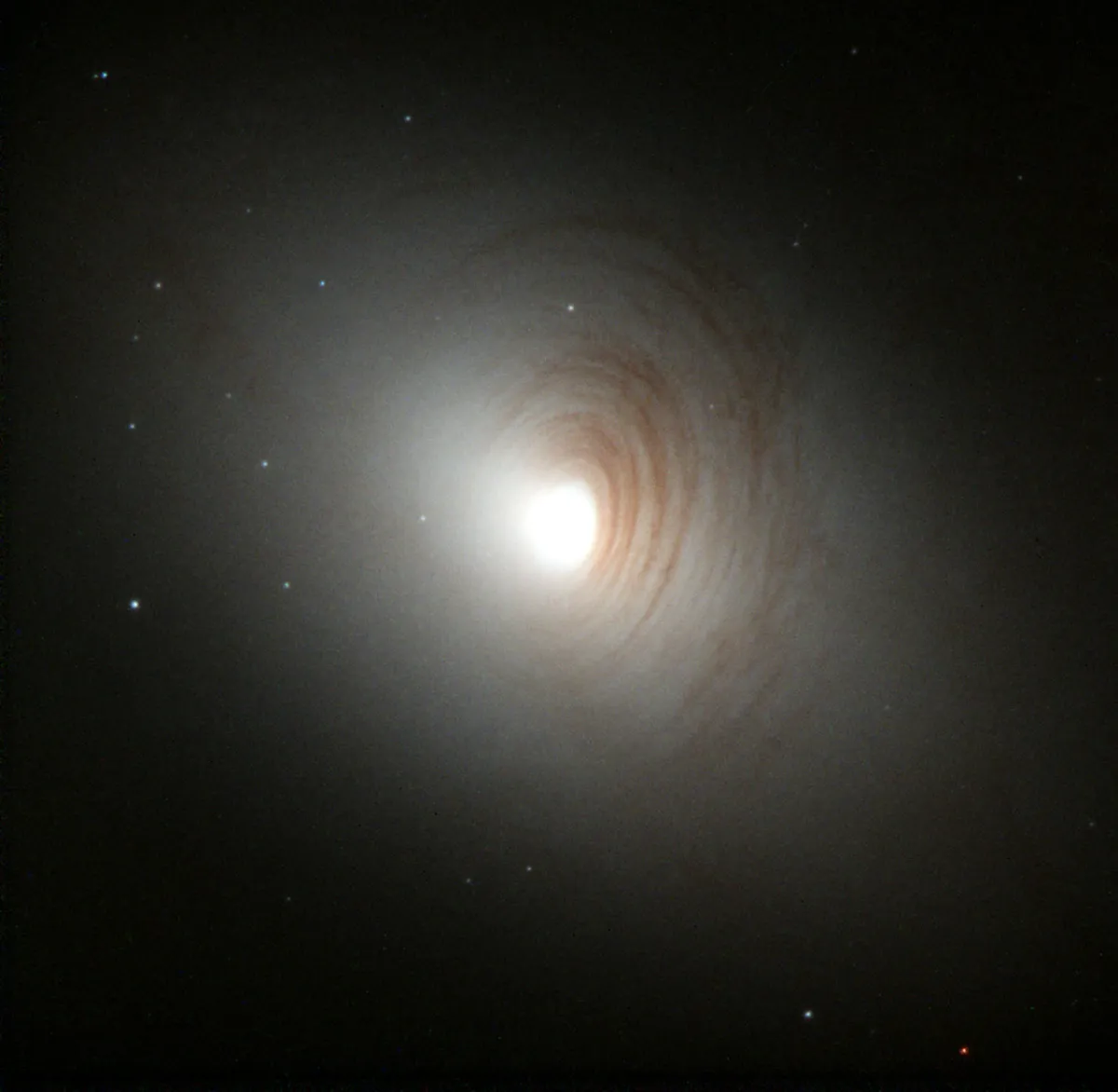
Galaxy NGC 2787

History
This galaxy was discovered by William Herschel on 3 December 1788 using his selfmade reflecting telescope with 18.7 inch aperture and 20 feet focal length. He classified the galaxy as bright nebula and listed it as I 216 with the following notes: «Very bright, pretty large, irregular figure, resolvable, much brighter in the middle. Towards the south following, within the nebulosity, is a very small star.» [465]
John Herschel observed the galaxy on 28 October 1831, listed it as h 570 and noted: «faint; extended in parallel; pretty suddenly brighter in the middle; 30" diameter.» [466]
Physical Properties
| Designation | NGC 2787 |
| Type | Gx (SB0-a) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 09h 19m 18.4s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +69° 12' 13" |
| Diameter | 3.1 × 1.8 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 11.8 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 10.7 mag |
| Surface brightness | 12.5 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 111° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.002322 |
| Distance derived from z | 9.81 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 10.240 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | B, pL, lE 90°, mbM, r, vS * sf inv |
| Identification, Remarks | WH I 216; h 570; GC 1781; UGC 4914; MCG 12-9-39; CGCG 332-41; IRAS 09148+6924 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 2787 is located in constellation Ursa Maior. On 7 February it is in opposition with the Sun and is therefore highest in the sky at local midnight.