NGC 1407 Galaxy Group
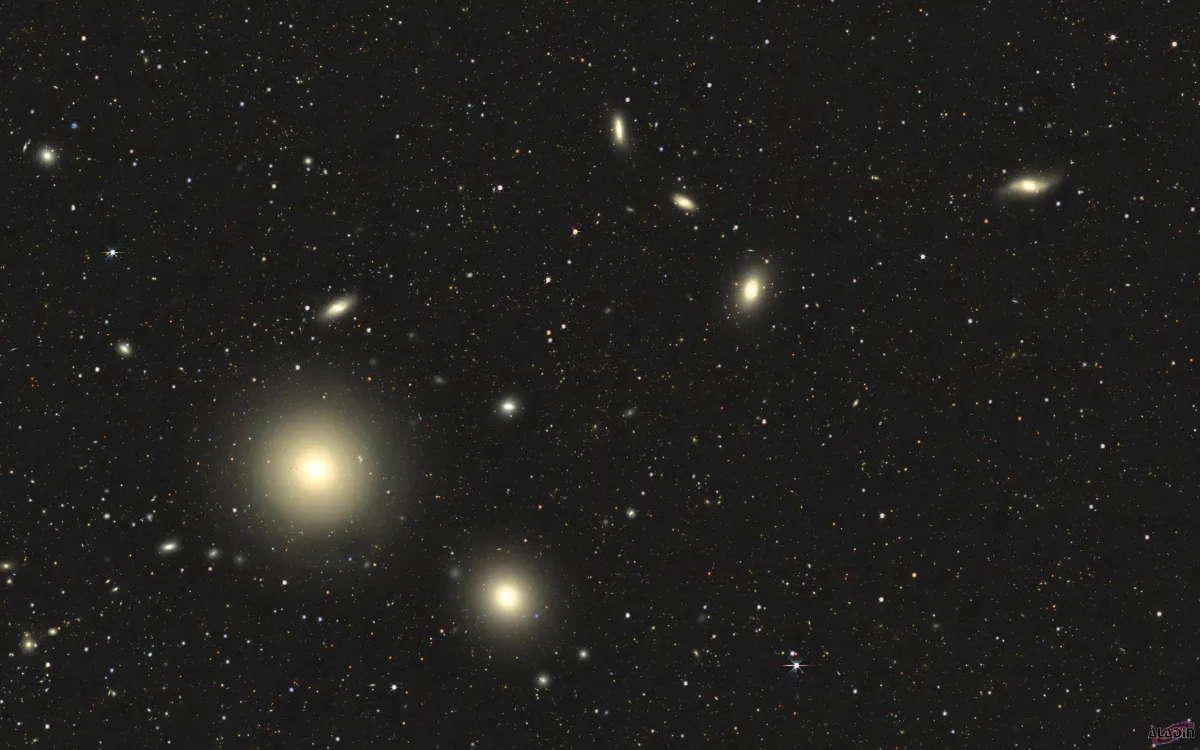

History
The galaxy NGC 1407 was discovered on 6 October 1785 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel with his 18.7 inch reflector telescope. He listed it as «bright nebula» I 107 and the notes: «Very bright, round, bright nucleus in the middle, 1.5' diameter.» In the same night he also added an entry for NGC 1393 (WH III 451) as «very faint, small, round.» About one year later on 20 September 1786 Herschel revisited this area and listed NGC 1400 (WH II 593) with the notes: «Pretty bright, pretty small, round, resembling I 107, but less.» [464]
On 11 December 1835 John Herschel discovered NGC 1383 (h 2562) and recorded: «Pretty faint, very small, round, pretty suddenly much brighter middle.» [11]
In 1886 Francis Leavenworth discovered NGC 1391, NGC 1394 and NGC 1402 the 26" refractor at the Leander McCormick Observatory. IC 339, IC 343, IC 345, IC 346 were discovered in 1887 by Ormond Stone and Frank Muller at the same observatory. [277]
Physical Properties
NGC 1407 is a massive early-type elliptical galaxy, the brightest member of the Eridanus A galaxy group and located at its center. The galaxy shows a complex kinematical structure, consisting of the outer areas, an embedded disc within a radius of ∼60 arcsec, and a kinematically decoupled core with a radius of less than 30 arcsec, which rotates in the opposite direction than the rest of the galaxy. This structure is likely to have formed through either a major merger or a series of minor mergers early in the lifetime of the galaxy. [728, 729]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 1383 | 03 37 39.2 | -18 20 22 | Gx (SB0) | 13.5 | 12.5 | 1.0 | 12.9 | 1.9 × 0.8 | 91 | 0.006498 | 27.45 | pF, S, R, psmbM | h 2562; GC 742; ESO 548-53; MCG -3-10-15 | |
| NGC 1391 | 03 38 52.9 | -18 21 16 | Gx (SB0) | 14.4 | 13.4 | 1.0 | 12.7 | 1.2 × 0.5 | 65 | 0.014440 | 60.99 | eF, S, R, gbMN | ESO 548-59; MCG -3-10-20; NPM1G -18.0142 | |
| NGC 1393 | 03 38 38.4 | -18 25 43 | Gx (SB0) | 13.0 | 12.0 | 1.0 | 12.9 | 1.7 × 1.3 | 170 | 0.007175 | 30.31 | F, S, R, glbM | WH III 451; h 2565; GC 745; ESO 548-58; MCG -3-10-19 | |
| NGC 1394 | 03 39 06.7 | -18 17 32 | Gx (S0) | 13.8 | 12.8 | 1.0 | 12.1 | 1.3 × 0.4 | 5 | 0.014153 | 59.78 | vF, vS, E 170°, sbMN | ESO 548-60; MCG -3-10-21 | |
| NGC 1400 | 03 39 30.7 | -18 41 17 | Gx (E-S0) | 11.9 | 11.0 | 0.9 | 12.5 | 2.5 × 2.1 | 40 | 0.001861 | 7.86 | 22.920 | cB, pS, R, psmbM | WH II 593; h 2567; GC 747; ESO 548-62; MCG -3-10-22; IRAS 03372-1850 |
| NGC 1402 | 03 39 30.4 | -18 31 37 | Gx (SB0) | 14.4 | 13.6 | 0.8 | 12.6 | 0.8 × 0.6 | 88 | 0.014333 | 60.54 | eF, vS, R | ESO 548-61; MCG -3-10-23; IRAS 03372-1841 | |
| NGC 1407 | 03 40 11.8 | -18 34 49 | Gx (E1) | 10.7 | 9.7 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 4.6 × 4.3 | 35 | 0.005934 | 25.06 | 23.110 | vB, L, R, svmbMN | WH I 107; h 2570; GC 752; ESO 548-67; MCG -3-10-30 |
| IC 339 | 03 38 01.9 | -18 23 59 | * | 12.4 | eF, eS, stell N | ESO 548-*55 | ||||||||
| IC 343 | 03 40 07.1 | -18 26 38 | Gx (SB0-a) | 14.1 | 13.2 | 0.9 | 13.3 | 1.6 × 0.8 | 118 | 0.006141 | 25.94 | eF, vS, lE 90°, dif | ESO 548-66; MCG -3-10-29 | |
| IC 345 | 03 41 09.1 | -18 18 52 | Gx (S0-a) | 14.7 | 13.8 | 0.9 | 13.0 | 0.8 × 0.7 | 42 | 0.004453 | 18.81 | eF, vS, iR, gbM | ESO 548-74; MCG -3-10-32; NPM1G -18.0146 | |
| IC 346 | 03 41 24.9 | -18 22 16 | NF | vF, eS |
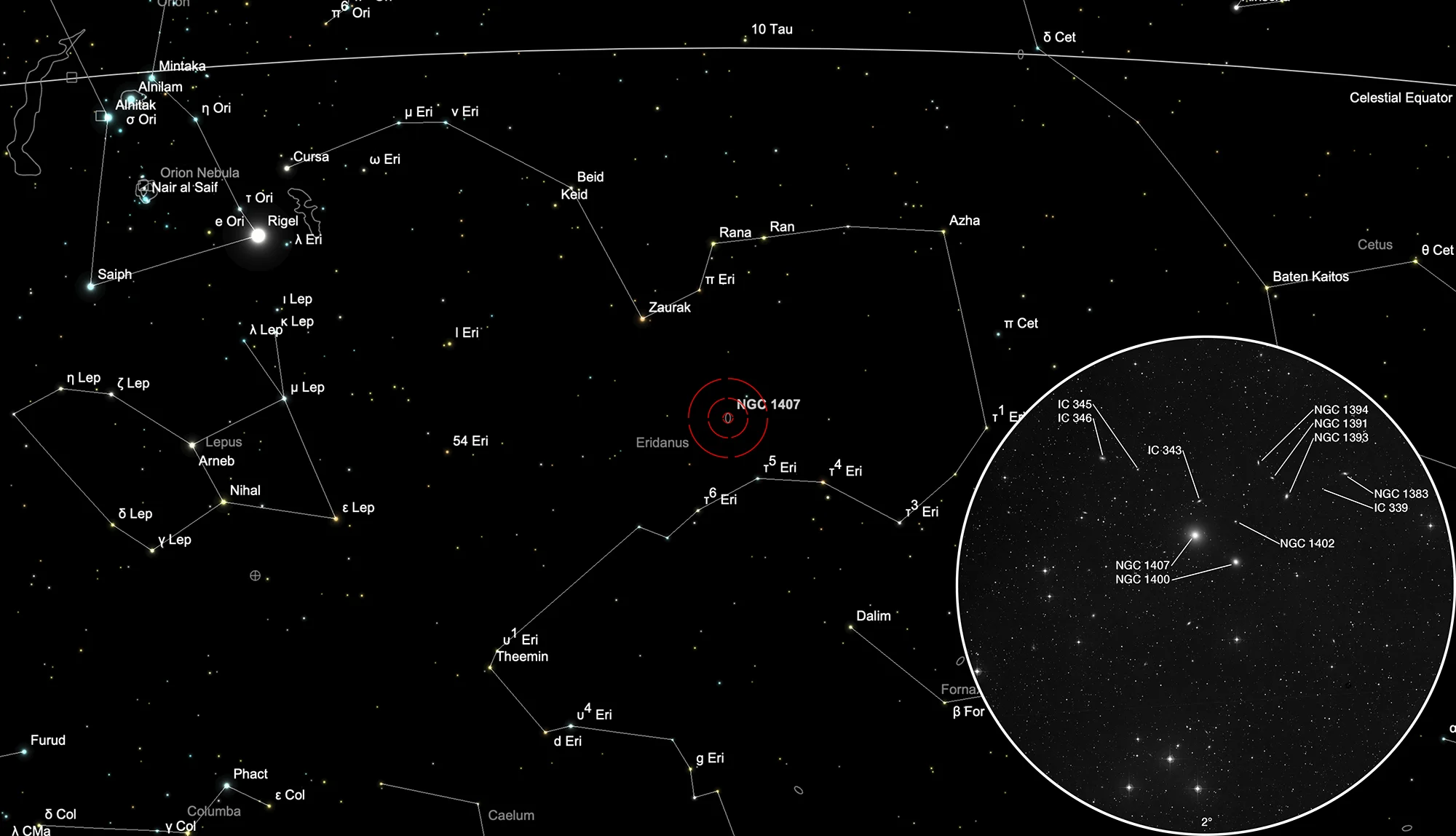
Finder Chart
The galaxies including NGC 1407 are located in the constellation Eridanus. On 20 November these are in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. Visible from your location in the months: July to April.