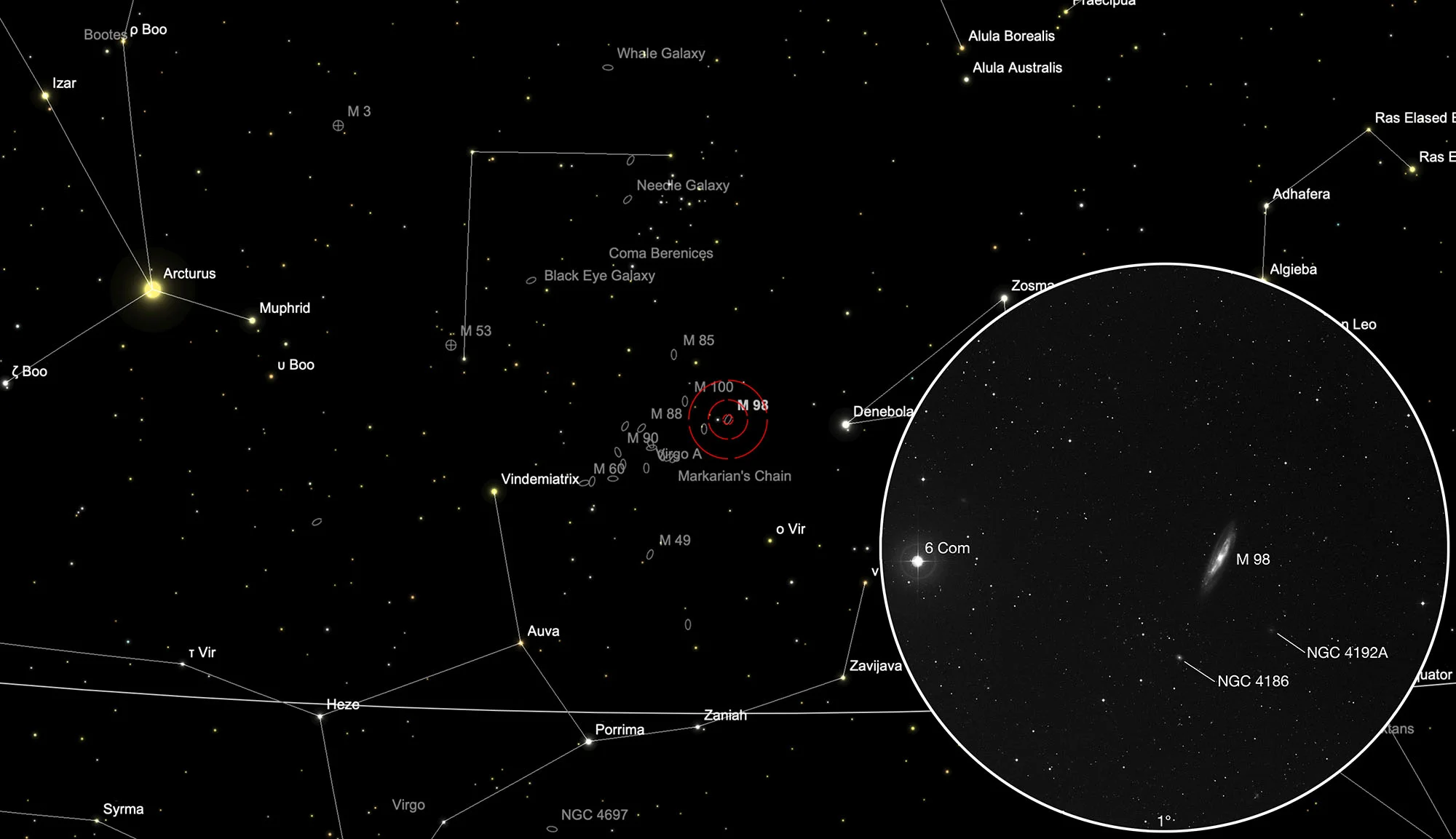
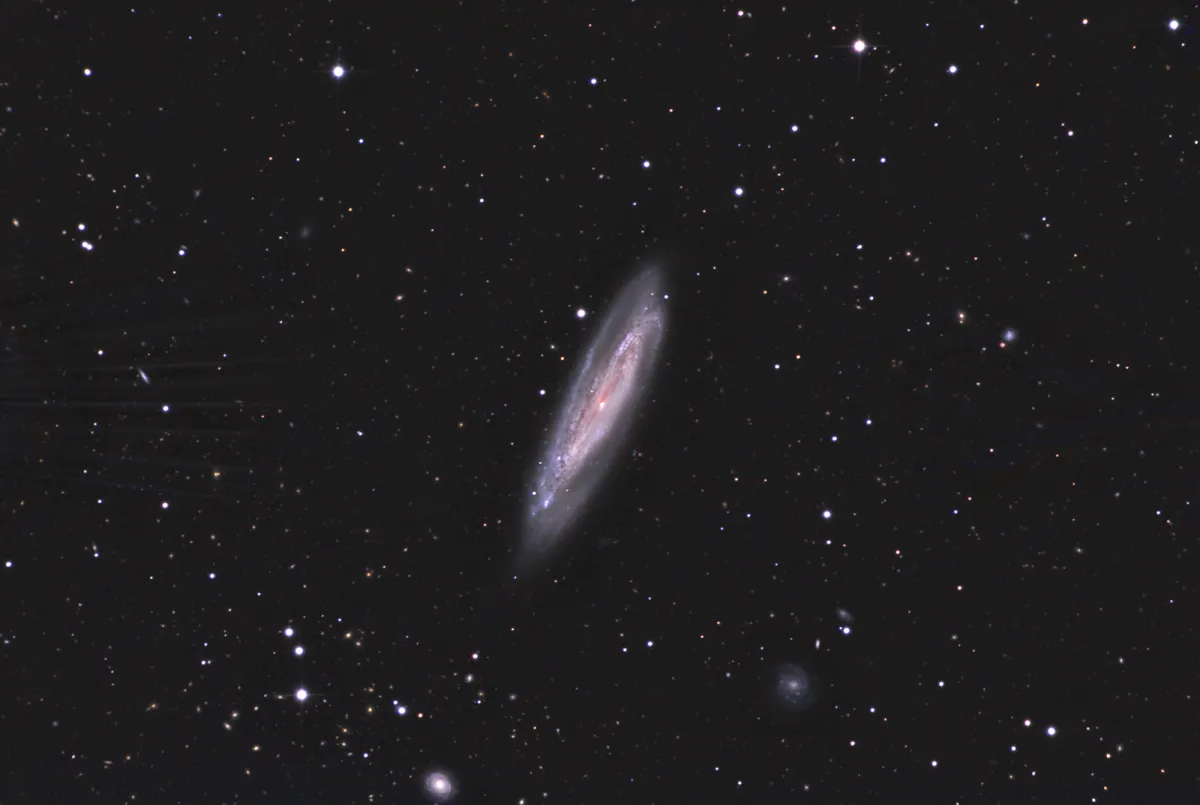
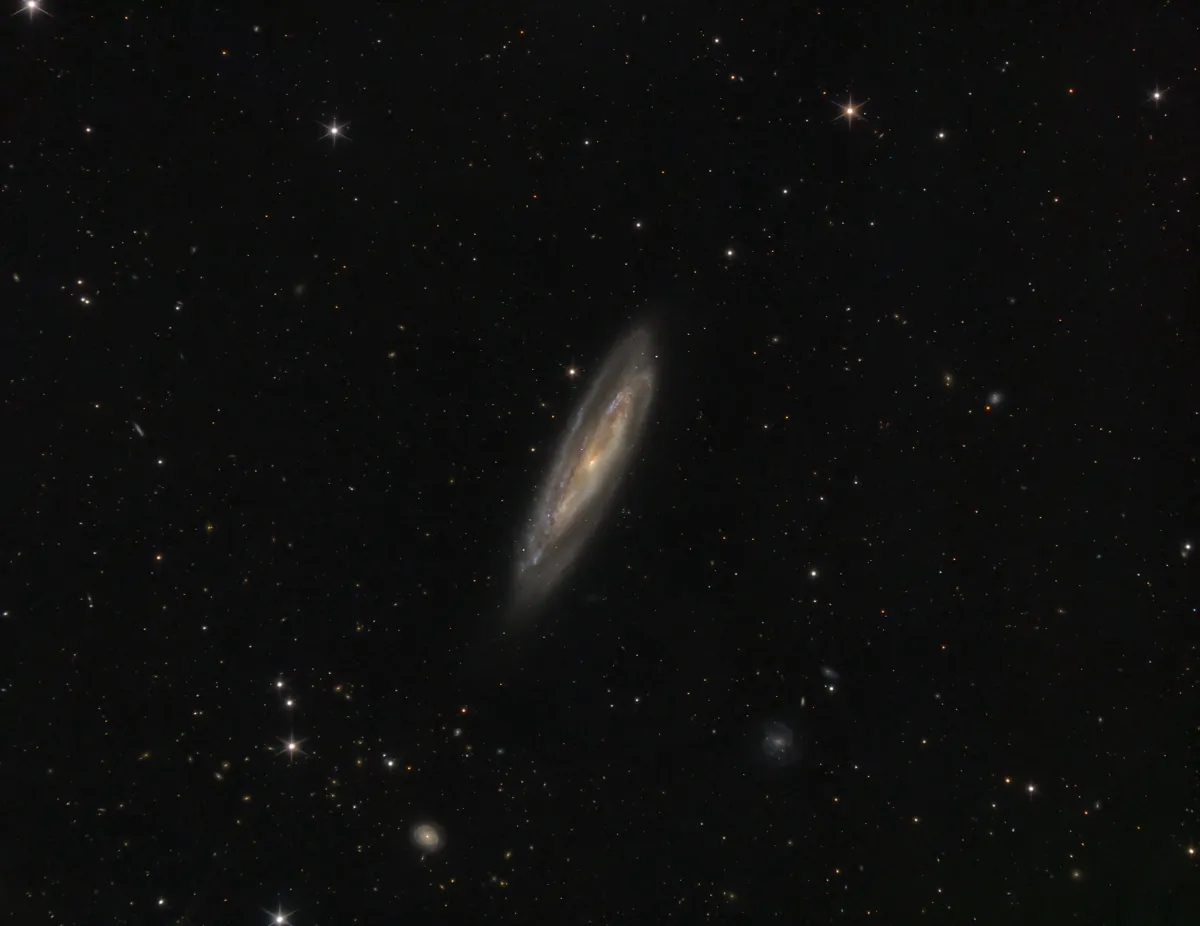
Galaxy Messier 98
History
M 98 was discovered by Pierre Méchain on 15 March 1781 and cataloged by Charles Messier on April 13, along with M 99 and M 100. He noted: «Nebula without a star, of very weak light, above the northern wing of the Jungfrau, on the parallel and next to the star no. 6, fifth size in the hair of Berenike, according to Flamsteed. M. Méchain saw him on 15 March 1781.» [281]


Physical Properties
The spiral galaxy M 98 is of the morphological type SAB(s)ab, which we see obliquely from the edge. It has an active core of the LINER type (Low-ionization nuclear emission-line region), is a Seyfert type 3 galaxy and numerous star formation regions with many young, hot, blue stars. It contains about one trillion (1012) stars and is about 14 Mpc (45 million light years) away. It is approaching us at a speed of 142 km/s. [194, 292]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4192 | 12 13 47.8 | +14 53 58 | Gx (SBb) | 11.0 | 10.1 | 0.9 | 13.5 | 9.8 × 2.8 | 155 | -0.000474 | 15.990 | B, vL, vmE 152°, vsvmbM | h 1132; GC 2786; M 98; UGC 7231; MCG 3-31-79; IRAS 12112+1510; CGCG 98-108; VCC 92 | |
| NGC 4192 A | 12 13 26.2 | +14 46 20 | Gx (Scd) | 15.7 | 15.0 | 0.7 | 15.2 | 1.3 × 1.1 | 75 | 0.006921 | 29.23 | 34.600 | B, vL, vmE 152°, vsvmbM | h 1132; GC 2786; UGC 7223; MCG 3-31-76; VCC 81 |
| NGC 4192 B | 12 14 06.4 | +14 43 33 | dup | 14.6 | 13.8 | 0.8 | 13.4 | 1 × 0.8 | 60 | 0.026292 | 111.0 | 98.700 | B, vL, vmE 152°, vsvmbM | h 1132; GC 2786; NGC 4186; UGC 7240; MCG 3-31-81; CGCG 98-111; VCC 101 |
Further Galaxies in that Area
In addition to M 98, there are two smaller, much more distant galaxies: NGC 4186 was discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1877. It is of the morphological type SA (s) from? and is approximately 112 Mpc (365 million light years) away. NGC 4192A (UGC 7223) is located 35 Mpc (114 million light years) away. [194, 196]
Finder Chart
M 98 is located in the constellation Coma Berenices between the two bright stars Vindemiatrix (ε Virginis) and Denebola (β Leonis), about a third closer to Denebola, about half a degree west of the 5 mag bright star 6 Comae Berenices . The best time for observation is November to September.