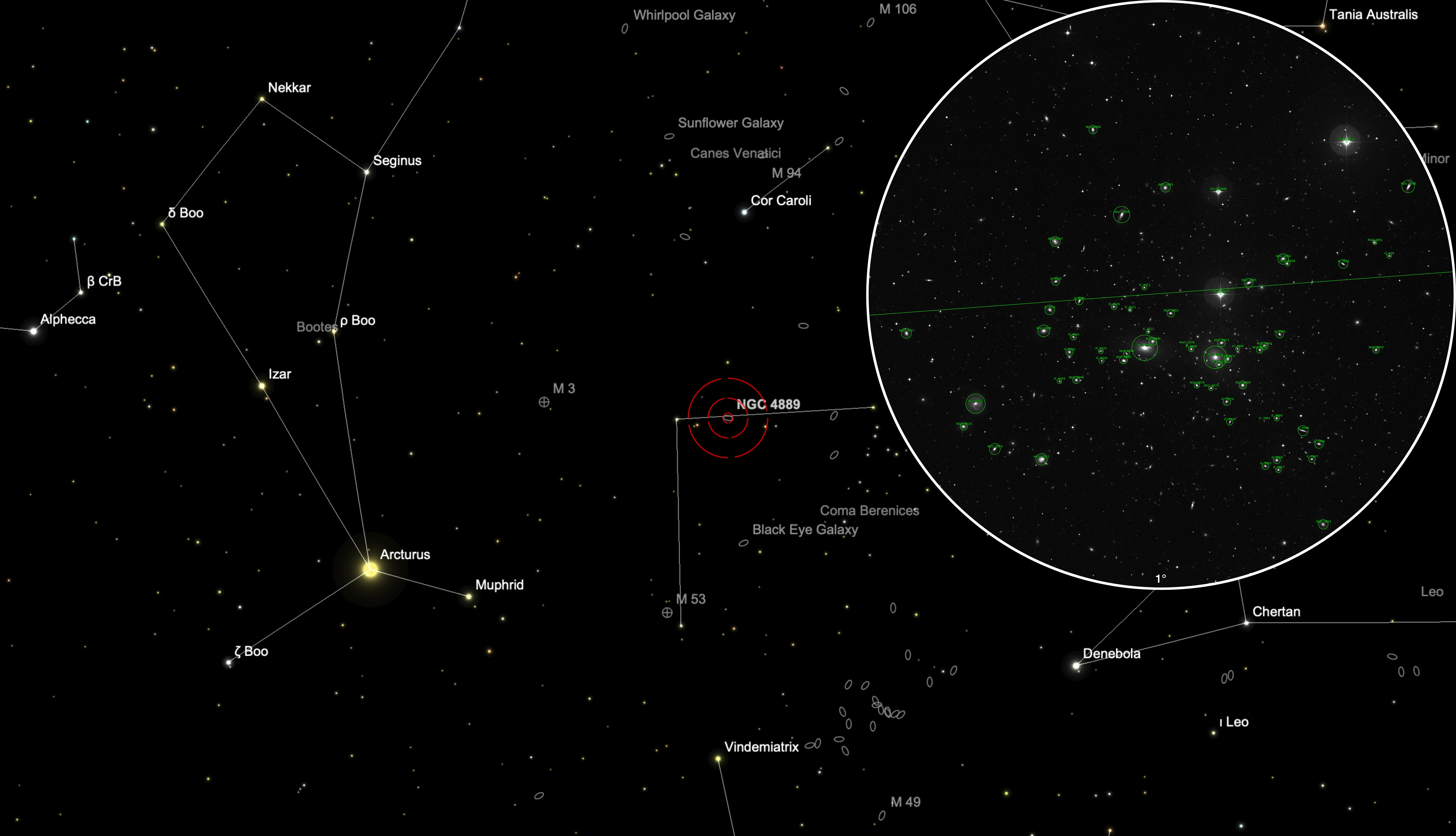
Galaxies NGC 4874/4889 & Coma Galaxy Cluster


History
On 11 April 1785 William Herschel discovered total 72 nebulae using his 18.7-inch reflecting telescope, most of them he classified as faint nebulae (class II) and very faint nebulae (class II). Among those discovered nebulae were: NGC 4864, 4874, 4889, 4908, 4911, 4921, 4923 and 4927. John Herschel verified his father's observations on 13 April 1831 and added four more nebulae: NGC 4853, 4869, 4894 and 4898. [364, 466]
Heinrich d'Arrest conducted multiple observations from May 1863 through April 1885 using the 11-inch refractor at Copenhagen Observatory to verify the nebulae discovered by the two Herschels. The following 17 nebulae were added to Dreyer's «New General Catalogue»: NGC 4848, 4850, 4851, 4854, 4858, 4860, 4865, 4867, 4871, 4872, 4873, 4881, 4886, 4895, 4906, 4907 and 4919. D'Arrest was the first to recognize the Coma assemblage of galaxies as a cluster and wrote: «The nebulae are incredibly numerous and dense and despite being faint, they have a diversity one cannot imagine a priori. Sometimes, in the most favourable moments, I had the very definite impression that the nebulae, often only a few arcseconds in diameter, are intermingled with larger, roung, oblong, star-shaped or cometary ones, like oysters packed together in a barrel.» [313, 364]

In May 1885, Guillaume Bigourdan observed this galaxy cluster with the 12.4-inch refractor at the Paris Observatory and discovered additional nebulae: NGC 4875, 4876, 4883, and 4896 were added by Dreyer in his «New General Catalogue» in 1888. Observations from April 1891 later appeared in Dreyer's two «Index Catalogue»: IC 839, IC 4051, and IC 4045. [313, 314, 315, 364]
Using the 18-inch refractor at the Strasbourg Observatory Hermann Kobold discovered in April/May 1895 and 1896 many more nebulae which were added in 2010 by Dreyer to his «Second Index Catalogue»: IC 3943, 3946, 3947, 3949, 3955, 3957, 3959, 3960, 3963, 3964, 3968, 3973, 3976, 3998, 4011, 4012, 4021, 4026, 4030, 4033, 4040, 4041, 4042, and 4044. [315, 364]
Physical Properties
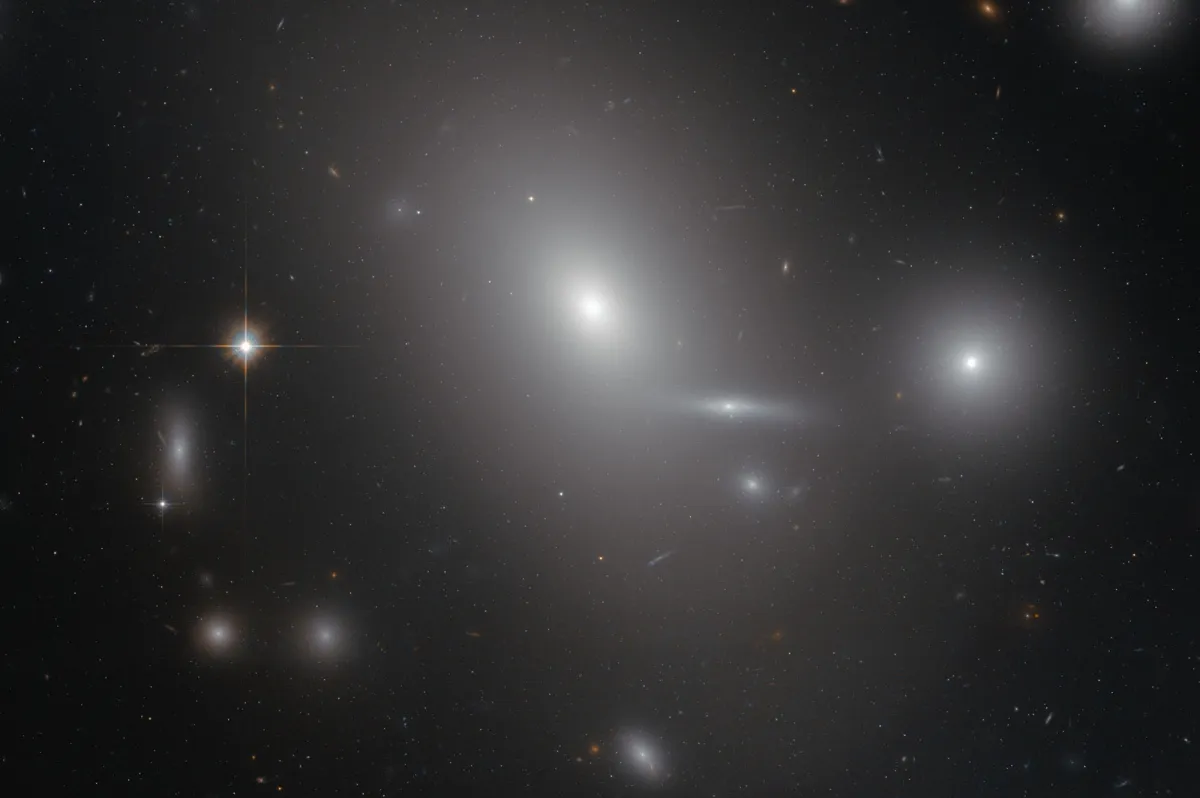
NGC 4889 is a giant elliptical galaxy, about two and a half times larger than the Milky Way. In the centre of the featureless looking galaxy NGC 4899 lies a supermassive black hole with a mass 21 billion times greater than the Sun. Its event horizon is estimated with a diameter of approximately 130 billion kilometres, circa 15 times the diameter of Neptune’s orbit from the Sun. For comparison: The black hole at the centre of our galaxy is thought to be 4 million times more massive than the Sun with an event horizon just one fifth the orbit of Mercury. The black hole in the centre NGC 4889 of is currently inactive. It has stopped sucking in material and new stars are actually forming and orbiting around it. [261]
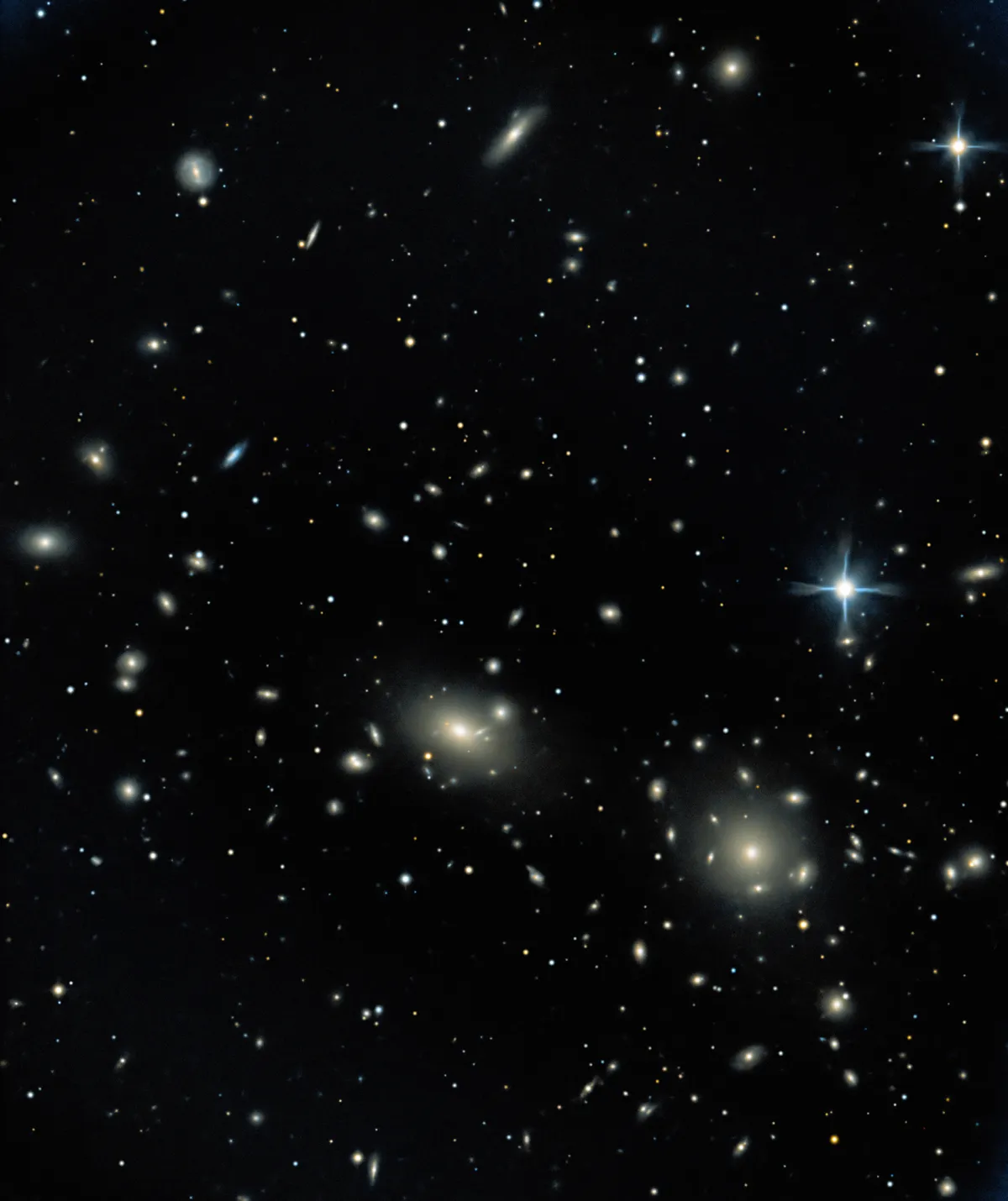
The two galaxies NGC 4874 and NGC 4889 dominate the gravitational centre of the Coma Cluster of galaxies (Abell 1656, ACO 1656). It is located circa 300 million light-years and according to Simbad it contains more than 3000 galaxies, most of them elliptical. [145] In the following table all the galaxies with NGC/IC numbers as shown in the 1° close-up of the finder chart are listed.
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4848 | 12 58 05.7 | +28 14 33 | Gx (SBc) | 14.4 | 13.7 | 0.7 | 13.3 | 1.6 × 0.5 | 158 | 0.023513 | 99.32 | pF, S, lE | GC 5686; UGC 8082; MCG 5-31-39; CGCG 160-55; DRCG 27-220; KUG 1255+285; IRAS 12556+2830 | |
| NGC 4850 | 12 58 21.7 | +27 58 06 | Gx (S0) | 15.2 | 14.2 | 1.0 | 13.2 | 0.7 × 0.5 | 63 | 0.020087 | 84.85 | F, S, R | GC 5688; MCG 5-31-40; CGCG 160-63; NPM1G +28.0251; DRCG 27-137 | |
| NGC 4851 1 | 12 58 21.8 | +28 08 52 | Gx (S0) | 15.2 | 14.2 | 1.0 | 11.3 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 112 | 0.026221 | 110.7 | F, vS, r | GC 5689; CGCG 160-61; DRCG 27-199 | |
| NGC 4851 2 | 12 58 22.3 | +28 09 07 | Gx (S0) | 16.0 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 11.8 | 0.3 × 0.2 | 100 | 0.022372 | 94.50 | F, vS, r | GC 5689; DRCG 27-198 | |
| NGC 4853 | 12 58 35.4 | +27 35 45 | Gx (E-S0) | 14.4 | 13.6 | 0.8 | 13.0 | 0.8 × 0.7 | 81 | 0.025604 | 108.1 | F, S, R, pslbM | h 1496; GC 3336; UGC 8092; MCG 5-31-48; CGCG 160-68; DRCG 27-43; IRAS 12561+2752; 2ZW 67; KUG 1256+278B | |
| NGC 4854 | 12 58 47.6 | +27 40 27 | Gx (SB0) | 14.9 | 13.9 | 1.0 | 13.7 | 1.2 × 0.8 | 57 | 0.027933 | 117.9 | 94.400 | vF, pL, com | GC 5690; MCG 5-31-49; CGCG 160-70; DRCG 27-58 |
| NGC 4858 | 12 59 02.3 | +28 06 55 | Gx (SBb) | 15.7 | 15.2 | 0.5 | 13.6 | 0.5 × 0.4 | 36 | 0.031475 | 132.9 | F, vS, p of D neb | GC 5691; MCG 5-31-51; CGCG 160-213; DRCG 21-195; IRAS 12566+2823 | |
| NGC 4860 | 12 59 04.0 | +28 07 24 | Gx (E2) | 14.6 | 13.5 | 1.1 | 14.1 | 0.9 × 0.8 | 126 | 0.026618 | 112.4 | 94.400 | pF, S, R, f of D neb | GC 5693; MCG 5-31-54; CGCG 160-215; DRCG 27-194 |
| NGC 4864 | 12 59 13.2 | +27 58 35 | Gx (E6) | 14.6 | 13.6 | 1.0 | 11.8 | 0.7 × 0.5 | 129 | 0.022532 | 95.17 | 94.400 | F, S, p of 2 | h 1500; GC 3343; MCG 5-31-58; CGCG 160-221; ARAK 397; DRCG 27-159 |
| NGC 4865 | 12 59 20.0 | +28 05 03 | Gx (E3) | 14.6 | 13.7 | 0.9 | 12.8 | 0.9 × 0.5 | 115 | 0.015677 | 66.22 | vF, vS, * 7·8 f 13s | GC 5694; UGC 8100; MCG 5-31-64; CGCG 160-224; DRCG 27-179 | |
| NGC 4867 | 12 59 15.5 | +27 58 14 | Gx (E3) | 15.4 | 14.5 | 0.9 | 13.5 | 0.5 × 0.4 | 3 | 0.015964 | 67.43 | 94.400 | vF, vS, stellar, f h 1500 | MCG 5-31-62; CGCG 160-222; DRCG 27-133 |
| NGC 4869 | 12 59 23.5 | +27 54 41 | Gx (E3) | 14.8 | 13.8 | 1.0 | 13.1 | 0.8 × 0.7 | 69 | 0.022879 | 96.64 | 94.400 | cF, S, R, * 7 n | WH II 388; h 1501; GC 3344; MCG 5-31-65; CGCG 160-225; DRCG 27-105 |
| NGC 4871 | 12 59 30.1 | +27 57 23 | Gx (S0) | 15.2 | 14.2 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 0.7 × 0.5 | 177 | 0.022445 | 94.81 | vF, vS, stell N | MCG 5-31-66; CGCG 160-227; DRCG 27-131 | |
| NGC 4872 | 12 59 35.8 | +27 57 34 | Gx (E0) | 12.6 | 11.7 | 0.9 | 13.1 | 1.9 × 1.9 | 0.023937 | 101.1 | 94.660 | pF, pS, R | WH II 389; h 1502; GC 3347; UGC 8103; MCG 5-31-70; CGCG 160-231; Z 1257.2+2814; DRCG 27-129 | |
| NGC 4873 | 12 59 32.9 | +27 59 00 | Gx (S0) | 15.1 | 14.1 | 1.0 | 13.1 | 0.8 × 0.6 | 105 | 0.019310 | 81.56 | vF, vS | MCG 5-31-69; CGCG 160-229; DRCG 27-155 | |
| NGC 4874 | 12 59 34.3 | +27 56 48 | Gx (SB0) | 15.4 | 14.4 | 1.0 | 15.2 | 0.5 × 0.3 | 123 | 0.023993 | 101.3 | 94.400 | F, h 1501 and 1502 p | GC 5695; MCG 5-31-68; CGCG 160-230; DRCG 27-130 |
| NGC 4875 | 12 59 38.1 | +27 54 27 | Gx (S0) | 15.7 | 14.7 | 1.0 | 12.3 | 0.4 × 0.3 | 123 | 0.026835 | 113.3 | vF, vS, stellar | CGCG 160-232; DRCG 27-104 | |
| NGC 4876 | 12 59 44.6 | +27 54 44 | Gx (E5) | 15.4 | 14.4 | 1.0 | 12.9 | 0.6 × 0.4 | 18 | 0.022275 | 94.09 | 94.400 | vF, vS, no Nucl | MCG 5-31-73; CGCG 160-234; ARAK 398; DRCG 27-124 |
| NGC 4881 | 12 59 57.9 | +28 14 47 | Gx (E0) | 14.6 | 13.6 | 1.0 | 13.5 | 1 × 1 | 0.022389 | 94.57 | F, S, lE, * 9 sp | GC 5696; UGC 8106; MCG 5-31-75; CGCG 160-238; DRCG 27-217 | ||
| NGC 4883 | 12 59 56.2 | +28 02 03 | Gx (SB0) | 15.4 | 14.3 | 1.1 | 12.1 | 0.5 × 0.3 | 97 | 0.027289 | 115.2 | vF, S, stellar | CGCG 160-237; DRCG 27-175 | |
| NGC 4886 | 13 00 04.6 | +27 59 11 | Gx (E0) | 14.8 | 13.9 | 0.9 | 14.0 | 0.6 × 0.6 | 0.021321 | 90.06 | 94.400 | F, S, R, II 391 f 4s | GC 5699; NGC 4882; MCG 5-31-76; CGCG 160-239; DRCG 27-151 | |
| NGC 4889 | 13 00 08.3 | +27 58 35 | Gx (E3) | 12.5 | 11.5 | 1.0 | 13.3 | 2.8 × 2 | 80 | 0.021665 | 91.51 | 101.77 | pB, pmE, bM, * 7 n | WH II 391; h 1507; GC 3351; NGC 4884; UGC 8110; MCG 5-31-77; CGCG 160-241; DRCG 27-148 |
| NGC 4894 | 13 00 16.7 | +27 58 01 | Gx (S0) | 16.1 | 15.2 | 0.9 | 12.6 | 0.5 × 0.1 | 27 | 0.015457 | 65.29 | pF, S, R | h 1510; GC 3354; CGCG 160-247; DRCG 27-122 | |
| NGC 4895 | 13 00 18.0 | +28 12 06 | Gx (S0/P) | 14.2 | 13.2 | 1.0 | 13.2 | 1.8 × 0.6 | 153 | 0.028326 | 119.6 | vF, S, R | GC 5701; UGC 8113; MCG 5-31-81; CGCG 160-249; DRCG 27-206 | |
| NGC 4895 A | 13 00 09.3 | +28 10 12 | Gx (E5) | 16.0 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 13.7 | 0.6 × 0.3 | 99 | 0.022619 | 95.54 | 94.400 | vF, S, R | GC 5701; CGCG 160-245; RB 167; DRCG 27-207 |
| NGC 4896 | 13 00 30.9 | +28 20 47 | Gx (E-S0) | 14.9 | 13.9 | 1.0 | 13.1 | 1 × 0.6 | 5 | 0.020054 | 84.71 | vF, vS, R, mbM | UGC 8117; MCG 5-31-84; CGCG 160-87; DRCG 27-232 | |
| NGC 4898 1 | 13 00 17.7 | +27 57 18 | Gx (E3) | 14.5 | 13.5 | 1.0 | 12.0 | 0.6 × 0.4 | 90 | 0.023026 | 97.26 | vF, S, close to h 1510 | MCG 5-31-82; CGCG 160-248; DRCG 27-121 | |
| NGC 4898 2 | 13 00 18.2 | +27 57 20 | Gx (E0) | 14.6 | 13.6 | 1.0 | 11.7 | 0.4 × 0.4 | 0.022219 | 93.85 | vF, S, close to h 1510 | MCG 5-31-82; CGCG 160-248; DRCG 27-121 | ||
| NGC 4906 | 13 00 39.8 | +27 55 26 | Gx (E3) | 15.1 | 14.1 | 1.0 | 12.7 | 0.5 × 0.5 | 0.025087 | 105.9 | 94.400 | vF, vS, * 15 p | GC 5702; CGCG 160-253; DRCG 27-118 | |
| NGC 4907 | 13 00 48.8 | +28 09 25 | Gx (SBb) | 14.4 | 13.6 | 0.8 | 13.5 | 1.1 × 1 | 42 | 0.019610 | 82.83 | eF, vS, * 13 att | GC 5703; MCG 5-31-89; CGCG 160-257; DRCG 27-205 | |
| NGC 4908 | 13 00 54.4 | +28 00 25 | Gx (E2) | 14.2 | 13.2 | 1.0 | 13.0 | 1 × 0.8 | 105 | 0.016658 | 70.36 | 101.11 | vF, vS | WH III 363; GC 5704; UGC 8129; MCG 5-31-90; CGCG 160-259; DRCG 27-143 |
| NGC 4911 | 13 00 56.3 | +27 47 25 | Gx (SBbc) | 13.6 | 12.8 | 0.8 | 13.3 | 1.2 × 1.1 | 127 | 0.026635 | 112.5 | 103.00 | 1st of 4, F, pL, * 11 2' np | WH II 392; GC 3364; UGC 8128; MCG 5-31-93; CGCG 160-260; DRCG 27-82; IRAS 12584+2803 |
| NGC 4911 A | 13 00 54.0 | +27 47 04 | Gx (S0) | 15.9 | 14.9 | 1.0 | 12.0 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 45 | 0.027883 | 117.7 | 1st of 4, F, pL, * 11 2' np | WH II 392; GC 3364; DRCG 27-62 | |
| NGC 4919 | 13 01 17.6 | +27 48 31 | Gx (S0) | 15.1 | 14.1 | 1.0 | 13.6 | 1.1 × 0.7 | 140 | 0.024464 | 103.3 | vF, vS, 2nd of 4 | GC 5708; UGC 8133; MCG 5-31-97; CGCG 160-94; DRCG 27-79 | |
| NGC 4921 | 13 01 26.3 | +27 53 08 | Gx (SBab) | 13.0 | 12.2 | 0.8 | 13.8 | 2.4 × 2.1 | 165 | 0.018286 | 77.24 | F, pL, 3rd of 4 | WH II 393; h 1516; GC 3368; UGC 8134; MCG 5-31-98; CGCG 160-95; DRCG 27-97 | |
| NGC 4923 | 13 01 31.8 | +27 50 49 | Gx (E/SB0) | 14.7 | 13.7 | 1.0 | 13.1 | 0.8 × 0.8 | 0.018293 | 77.27 | 94.400 | vF, 4th of 4 | WH II 394; h 1518; GC 3369; MCG 5-31-101; CGCG 160-97; DRCG 27-78 | |
| NGC 4927 | 13 01 57.6 | +28 00 22 | Gx (E-S0) | 14.8 | 13.8 | 1.0 | 12.3 | 0.6 × 0.4 | 15 | 0.025898 | 109.3 | vF | WH III 364; GC 3372; MCG 5-31-104; CGCG 160-105; DRCG 27-141 | |
| IC 839 | 12 58 15.0 | +28 07 35 | Gx (S0) | 15.8 | 14.8 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 0.6 × 0.3 | 92 | 0.024904 | 105.1 | stellar, 13m | CGCG 160-57; DRCG 27-200; DFOT 201 | |
| IC 3943 | 12 58 36.5 | +28 06 48 | Gx (S0-a) | 15.6 | 14.7 | 0.9 | 12.3 | 0.6 × 0.2 | 50 | 0.022646 | 95.66 | pF, vS, iF | CGCG 160-69; DRCG 27-197 | |
| IC 3946 | 12 58 49.1 | +27 48 35 | Gx (S0) | 15.1 | 14.0 | 1.1 | 12.5 | 0.7 × 0.4 | 80 | 0.019563 | 82.63 | F, pS, bM | MCG 5-31-50; CGCG 160-210; DRCG 27-91 | |
| IC 3947 | 12 58 52.0 | +27 47 08 | Gx (S0) | 15.4 | 14.4 | 1.0 | 11.2 | 0.3 × 0.2 | 95 | 0.018953 | 80.06 | vF, S | CGCG 160-211; NPM1G +28.0253; DRCG 27-72 | |
| IC 3949 | 12 58 56.6 | +27 49 59 | Gx (S0/P) | 15.1 | 14.3 | 0.8 | 12.4 | 1 × 0.2 | 73 | 0.025254 | 106.6 | 108.00 | F, pS, E | UGC 8096; MCG 5-31-52; CGCG 160-212; KUG 1256+281; DRCG 27-89 |
| IC 3955 | 12 59 06.1 | +27 59 46 | Gx (SB0) | 15.4 | 14.4 | 1.0 | 11.5 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 30 | 0.025611 | 108.1 | vF, S, N 14 mag | CGCG 160-216; DRCG 27-160 | |
| IC 3957 | 12 59 07.5 | +27 46 00 | Gx (E0) | 15.6 | 14.6 | 1.0 | 12.7 | 0.4 × 0.4 | 0.021135 | 89.27 | 94.400 | cF, vS, R, bM | MCG 5-31-60; CGCG 160-218; DRCG 27-70 | |
| IC 3959 | 12 59 08.3 | +27 47 01 | Gx (E0) | 15.2 | 14.2 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 0.5 × 0.5 | 0.023643 | 99.87 | 94.400 | F, pS, R, lbM | MCG 5-31-59; CGCG 160-217; DRCG 27-69 | |
| IC 3960 | 12 59 08.0 | +27 51 17 | Gx (SB0) | 15.9 | 14.9 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 0.4 × 0.4 | 0.022089 | 93.30 | vF, pS, diffic | MCG 5-31-55; CGCG 160-219; DRCG 27-109 | ||
| IC 3960 A | 12 59 09.8 | +27 52 01 | Gx (S0?) | 17.0 | 16.2 | 0.8 | 13.0 | 0.3 × 0.2 | 80 | 0.023069 | 97.44 | vF, pS, diffic | MCG 5-31-56 | |
| IC 3963 | 12 59 13.6 | +27 46 26 | Gx (S0) | 15.7 | 14.7 | 1.0 | 12.9 | 0.7 × 0.3 | 85 | 0.022846 | 96.50 | vF, vS, R, bM | MCG 5-31-61; CGCG 160-220; DRCG 27-68 | |
| IC 3964 | 12 59 13.6 | +27 51 04 | * | eF, vS | ||||||||||
| IC 3968 | 12 59 25.6 | +27 58 21 | Gx (S0) | 16.2 | 15.2 | 1.0 | 12.3 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 45 | 0.020387 | 86.11 | eF, vS, * 14 nr | RB 14; DRCG 27-157 | |
| IC 3973 | 12 59 30.7 | +27 53 06 | Gx (SB0) | 15.4 | 14.4 | 1.0 | 12.2 | 0.5 × 0.3 | 160 | 0.015861 | 67.00 | F, vS, R, N 13 mag | CGCG 160-228; DRCG 27-103 | |
| IC 3976 | 12 59 29.5 | +27 51 00 | Gx (E6) | 15.7 | 14.7 | 1.0 | 12.3 | 0.5 × 0.2 | 160 | 0.022899 | 96.72 | * 14 inv in vF neb | CGCG 160-226; DRCG 27-88 | |
| IC 3998 | 12 59 46.9 | +27 58 22 | Gx (SB0) | 15.6 | 14.6 | 1.0 | 13.5 | 0.8 × 0.5 | 10 | 0.031532 | 133.1 | eF, pS | CGCG 160-236; DRCG 27-152 | |
| IC 4011 | 13 00 06.6 | +28 00 11 | Gx (E0) | 16.1 | 15.1 | 1.0 | 13.7 | 0.5 × 0.5 | 0.024243 | 102.4 | 94.400 | eF, vS, N 15m | CGCG 160-242; DRCG 27-150 | |
| IC 4012 | 13 00 08.1 | +28 04 42 | Gx (E3) | 16.0 | 14.9 | 1.1 | 11.9 | 0.3 × 0.2 | 135 | 0.024243 | 102.4 | 94.400 | * 14 in vF neb | CGCG 160-244; DRCG 27-174 |
| IC 4021 | 13 00 14.9 | +28 02 26 | Gx (E0) | 15.9 | 14.8 | 1.1 | 12.9 | 0.4 × 0.4 | 0.019137 | 80.83 | 94.400 | * 14 in vF neb | MCG 5-31-80; CGCG 160-246; ARAK 399; DRCG 27-172 | |
| IC 4026 | 13 00 22.3 | +28 02 47 | Gx (SB0) | 15.6 | 14.6 | 1.0 | 11.8 | 0.3 × 0.3 | 0.027346 | 115.5 | * 14 in vF neb | CGCG 160-250; DRCG 27-170 | ||
| IC 4030 | 13 00 28.0 | +27 57 18 | Gx (S0) | 16.4 | 15.4 | 1.0 | 13.0 | 0.4 × 0.3 | 10 | 0.023296 | 98.40 | eF, vS, R, * 15 inv | RB 99; DRCG 27-119 | |
| IC 4033 | 13 00 28.6 | +27 58 20 | Gx (S0) | 16.0 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 13.2 | 0.7 × 0.3 | 95 | 0.025728 | 108.6 | eF, pS, R | RB 100; DRCG 27-147 | |
| IC 4040 | 13 00 38.1 | +28 03 24 | Gx (SBcd) | 15.4 | 14.8 | 0.6 | 13.2 | 1 × 0.3 | 153 | 0.026151 | 110.4 | 103.00 | vF, S, R, gbM | MCG 5-31-85; CGCG 160-252; IRAS 12582+2819; DRCG 27-169; KUG 1258+283; PGC 44792 ? |
| IC 4041 | 13 00 40.8 | +27 59 49 | Gx (E5) | 15.3 | 14.4 | 0.9 | 13.4 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 30 | 0.023723 | 100.2 | vF, pS | MCG 5-31-86; CGCG 160-254; PGC 44802; DRCG 27-145 | |
| IC 4042 | 13 00 42.7 | +27 58 18 | Gx (SB0) | 15.3 | 14.3 | 1.0 | 12.6 | 0.5 × 0.5 | 0.021321 | 90.06 | F, S, bM | CGCG 160-255; DRCG 27-144 | ||
| IC 4042 A | 13 00 42.8 | +27 57 48 | Gx (S0) | 16.3 | 15.3 | 1.0 | 13.2 | 0.4 × 0.4 | 0.027906 | 117.8 | 119.67 | F, S, bM | RB 113; DRCG 27-116 | |
| IC 4044 | 13 00 47.5 | +27 55 18 | Gx (S0-a) | 16.3 | 15.4 | 0.9 | 12.2 | 0.3 × 0.2 | 45 | 0.028590 | 120.7 | eF, S, lbM | RB 119; DRCG 27-117 | |
| IC 4045 | 13 00 48.8 | +28 05 25 | Gx (E4) | 15.0 | 13.9 | 1.1 | 12.9 | 0.8 × 0.5 | 115 | 0.023149 | 97.78 | 94.400 | pF, S, bM | MCG 5-31-88; CGCG 160-256; DRCG 27-168 |
| IC 4051 | 13 00 51.6 | +28 02 34 | Gx (E5) | 14.7 | 13.6 | 1.1 | 13.6 | 0.9 × 0.8 | 49 | 0.029330 | 123.8 | pF, S, R, bM, 4908 np | MCG 5-31-92; CGCG 160-258; DRCG 27-167 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 4889 and its companions of the Coma Cluster are located in the constellation Coma Berenices. The best observation time is December to September, when it is highest at night.
Visual Observation
350 mm Aperture: On approx. 2/3 degree field of view, 35 to 40 galaxies in the cluster Abell 1656 can be seen immediately without effort. — 14" PWO-Dobson, F:4.6 / TV-Nagler 13mm, 123x, 0.67°, Glaubenberg, 2. 4. 2005, Durchsicht ca. 6.7m, Eduard von Bergen