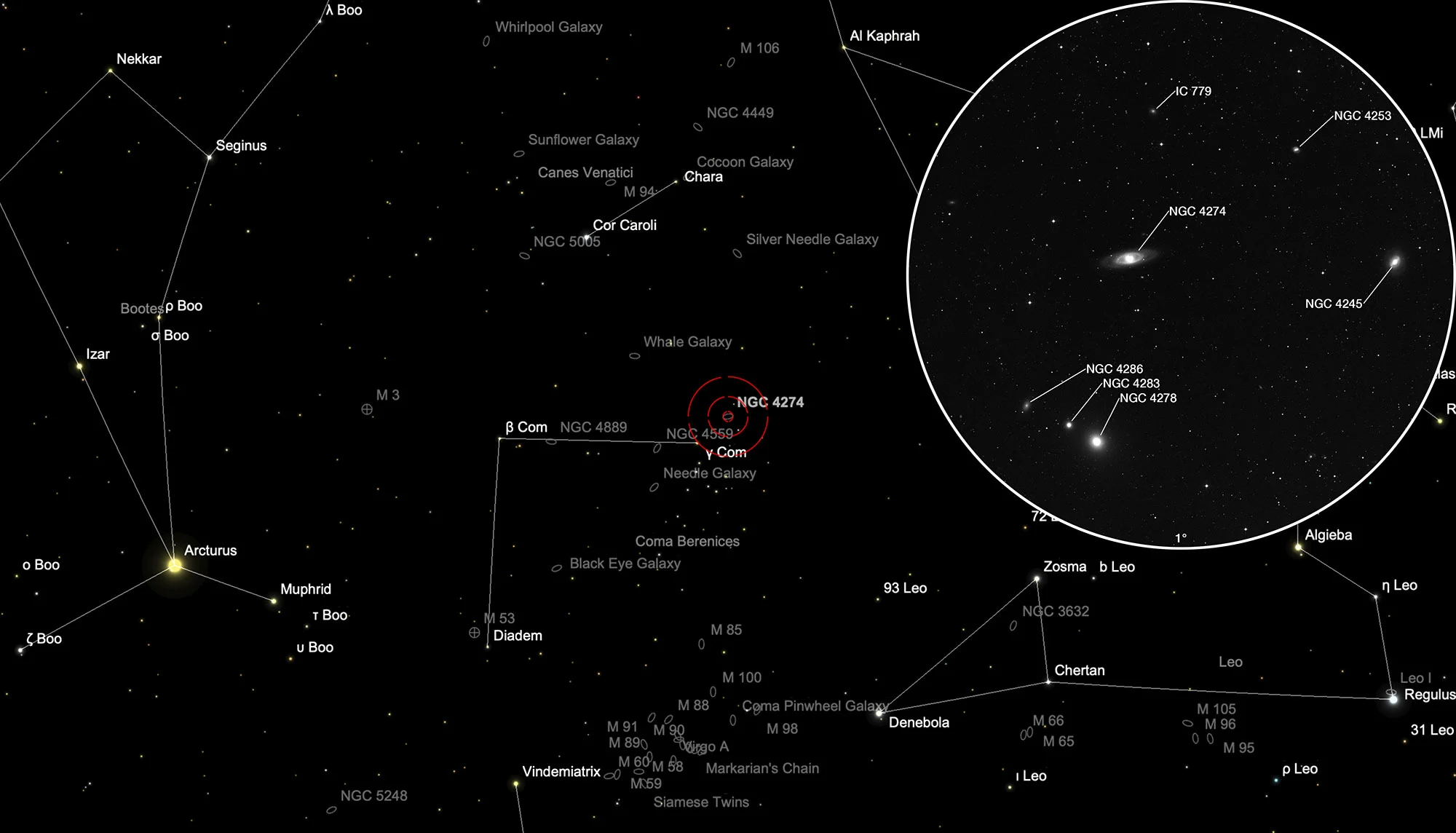
Galaxy NGC 4274

History
On 13 March 1785 William Herschel discovered the following galaxies using his 18.7 inch reflecting telescope: I 74 (NGC 4245), I 75 (NGC 4274), II 322 (NGC 4278), II 323 (NGC 4283) and III 300 (NGC 4286). The next month on April 11 he revisited and added two duplicate entries: I 90 (= II 322) and II 377 (= II 323). About 3 years later on 3 February 1788 Herschel discovered then II 377 (NGC 4283). [277, 463, 464] Finally, Truman Safford discovered IC 779 on 16 May 1866. On Mar 23, 1903 Max Wolf rediscovered NGC 4286 again which was added as IC 3181 as a duplicate. [196]
Physical Properties
According to HyperLEDA [134] the galaxies NGC 4245, NGC 4274, NGC 4278, NGC 4283 and NGC 4286 belong to the same group of galaxies (USGCU478), which is also known as the NGC 4274 Galaxy Group. [458] The distances for these galaxies are between 7 to 17 Mpc. The galaxy NGC 4253 is farther away (around 54 to 65 Mpc) and IC 779 also around 16 Mpc, but seems not to belong to that group. [145]
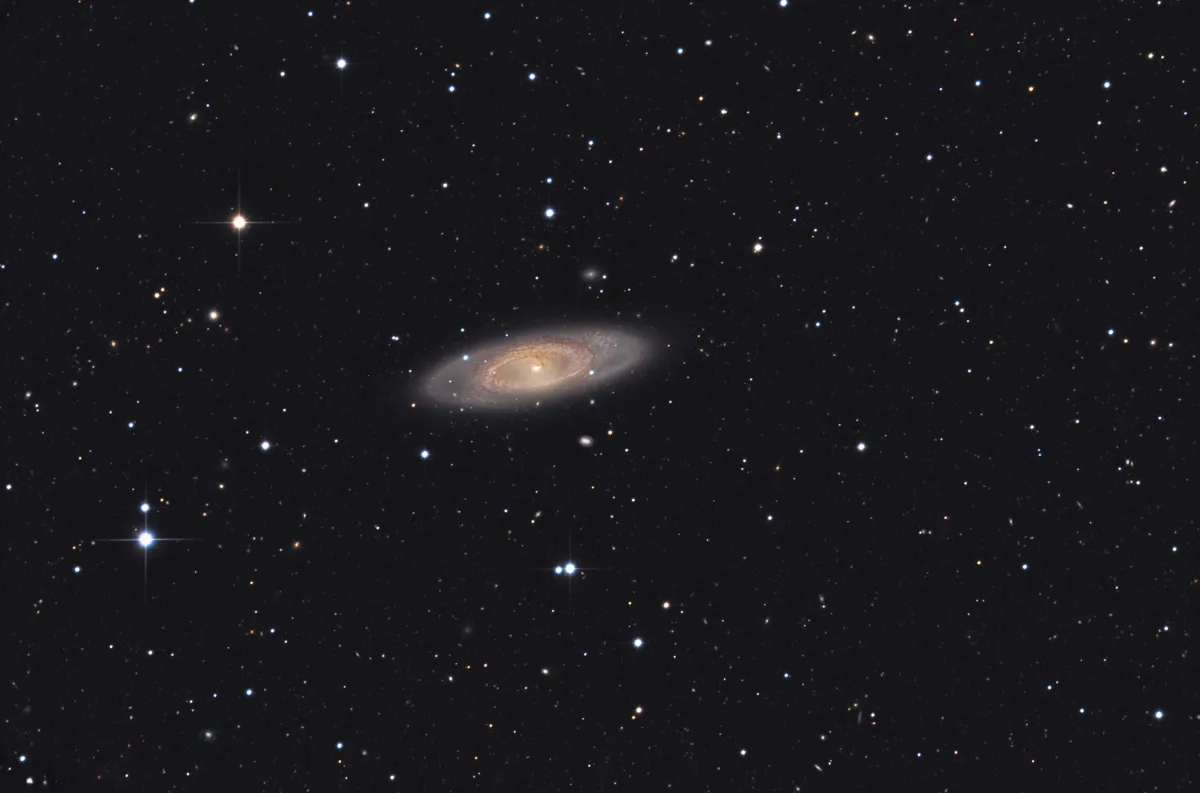
The galaxy NGC 4274 is a barred spiral galaxy with an inner and outer ring structure of morphological type (R)SB(r)ab with an active LINER type nucleus. [194] On 7 November 1999 the supernova SN 1999ev had been discovered. It reached 14.4 mag. [303]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4245 | 12 17 36.9 | +29 36 27 | Gx (SB0-a) | 12.3 | 11.4 | 0.9 | 13.3 | 2.9 × 2.2 | 165 | 0.002948 | 12.45 | 9.700 | cB, pL, vlE, smbM, r | WH I 74; h 1168; GC 2832; UGC 7328; MCG 5-29-49; CGCG 158-59; IRAS 12151+2952 |
| NGC 4253 | 12 18 26.4 | +29 48 47 | Gx (SBa) | 14.0 | 13.1 | 0.9 | 12.7 | 0.9 × 0.8 | 54 | 0.012929 | 54.61 | vF, vS, R | WH III 702; h 1172; GC 2837; UGC 7344; MCG 5-29-51; MK 766; IRAS 12159+3005; CGCG 158-61; KUG 1215+300 | |
| NGC 4274 | 12 19 50.8 | +29 36 49 | Gx (SBab) | 11.3 | 10.4 | 0.9 | 13.3 | 6.8 × 2.4 | 102 | 0.003102 | 13.10 | 16.830 | vB, vL, E 90°, mbMN | WH I 75; h 1185; GC 2851; UGC 7377; MCG 5-29-60; CGCG 158-71; IRAS 12173+2953 |
| NGC 4278 | 12 20 06.7 | +29 16 49 | Gx (E1) | 11.1 | 10.2 | 0.9 | 13.1 | 3.8 × 3.8 | 0.002165 | 9.14 | 15.180 | vB, pL, R, mbM, r, 1st of 3 | WH I 90, II 322; h 1186; GC 2855; UGC 7386; MCG 5-29-62; CGCG 158-77; IRAS 12175+2933 | |
| NGC 4283 | 12 20 20.6 | +29 18 39 | Gx (E0) | 13.0 | 12.1 | 0.9 | 12.9 | 1.5 × 1.5 | 0.003282 | 13.86 | 15.700 | B, S, R, bM, 2nd of 3 | WH II 323, II 377; h 1188; GC 2858=2859; UGC 7390; MCG 5-29-63; CGCG 158-80 | |
| NGC 4286 | 12 20 42.1 | +29 20 44 | Gx (S0-a) | 14.0 | 13.1 | 0.9 | 13.5 | 1.5 × 0.8 | 150 | 0.002148 | 9.07 | vF, 3rd of 3 | WH III 300; GC 2861=2863; IC 3181; UGC 7398; MCG 5-29-65; CGCG 158-83; KUG 1218+296 | |
| IC 779 | 12 19 38.7 | +29 52 58 | Gx (SBc) | 14.5 | 13.8 | 0.7 | 13.4 | 0.9 × 0.9 | 0.000741 | 3.13 | 16.520 | F | UGC 7369; MCG 5-29-53; CGCG 158-66 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 4274 can be found in the constellation Coma Berenices, circa 2° north-west of the 4.3 mag star γ Comae Berenices. It can best be seen in the months December to August.