Propeller Galaxy (NGC 7479)

History
The galaxy NGC 7479 was discovered on 19 October 1784 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel with his 18.7 inch reflecting telescope. He cataloged it as I 55 and noted: «Considerably bright, much extended in direction meridian, gradually brighter in the middle, 4' long 2' broad.» [464]
Physical Properties
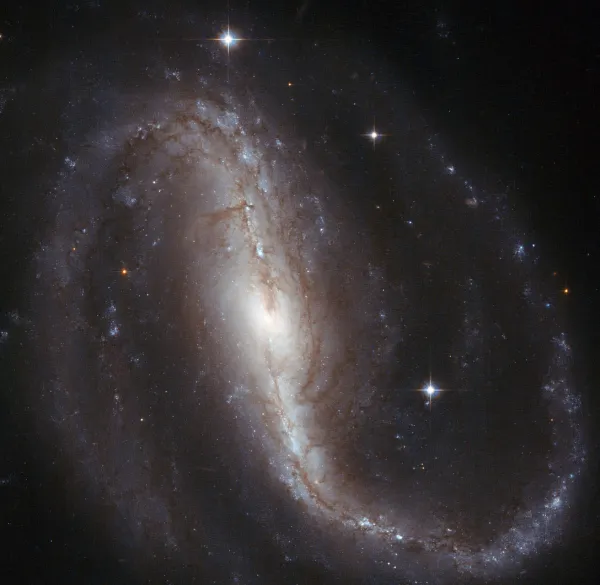

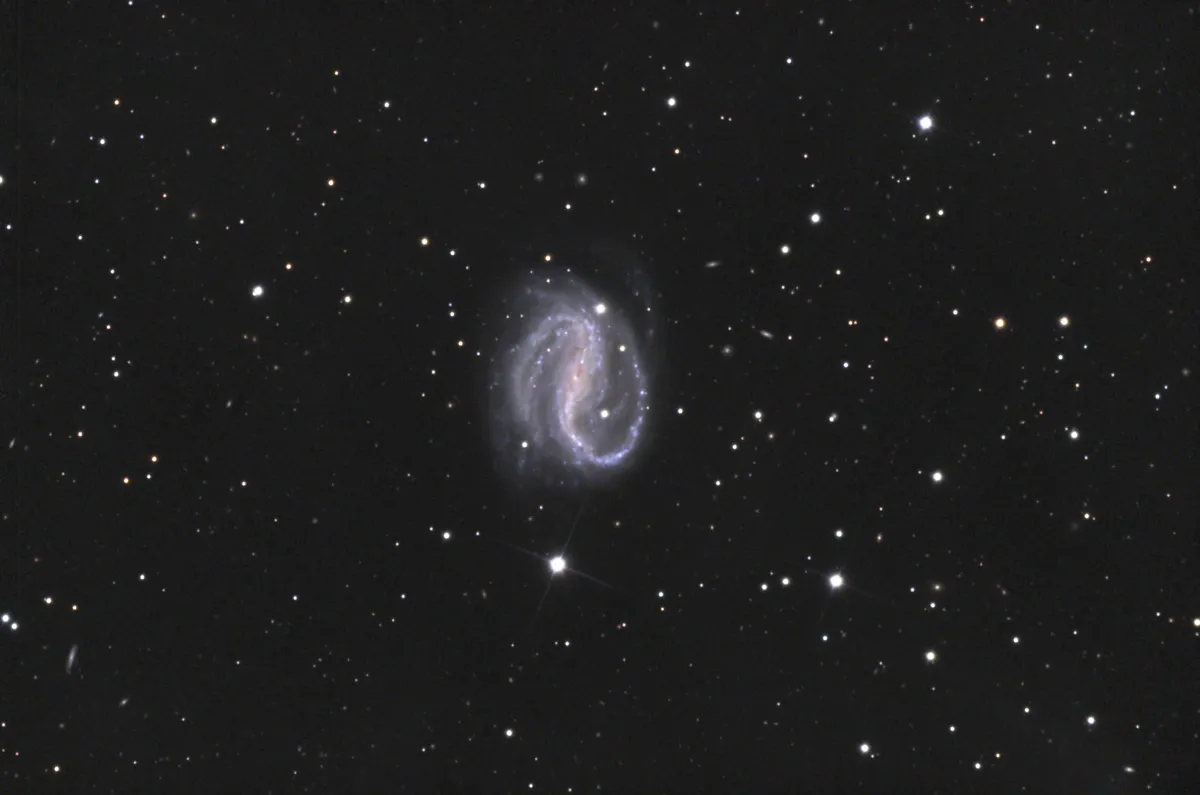
This is a Seyfert 2 galaxy at a distance of 30 Mpc to 36 Mpc. [145] The arms of this barred spiral galaxy spiral counterclockwise like a mirror-inverted «S». In the radio wave range, the galaxy rotates in the opposite direction. A jet of radiation curves in the opposite direction to the stars and dust in its arms. The radio jet in NGC 7479 is thought to have gone into its bizarre reverse spin after a merger with another galaxy. Star formation has been reignited as a result and the galaxy is experiencing starburst activity with many bright young stars in the spiral arms and disk. [440]
| Designation | NGC 7479 |
| Type | Gx (SBc) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 23h 04m 56.7s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +12° 19' 20" |
| Diameter | 4 × 3.1 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 11.6 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 10.9 mag |
| Surface brightness | 13.5 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 25° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.007942 |
| Distance derived from z | 33.55 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 33.850 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | pB, cL, mE 12°, bet 2 st |
| Identification, Remarks | WH I 55; h 2205; GC 4892; UGC 12343; MCG 2-58-60; CGCG 430-58; IRAS 23024+1203; KARA 1004; KUG 2302+120 |
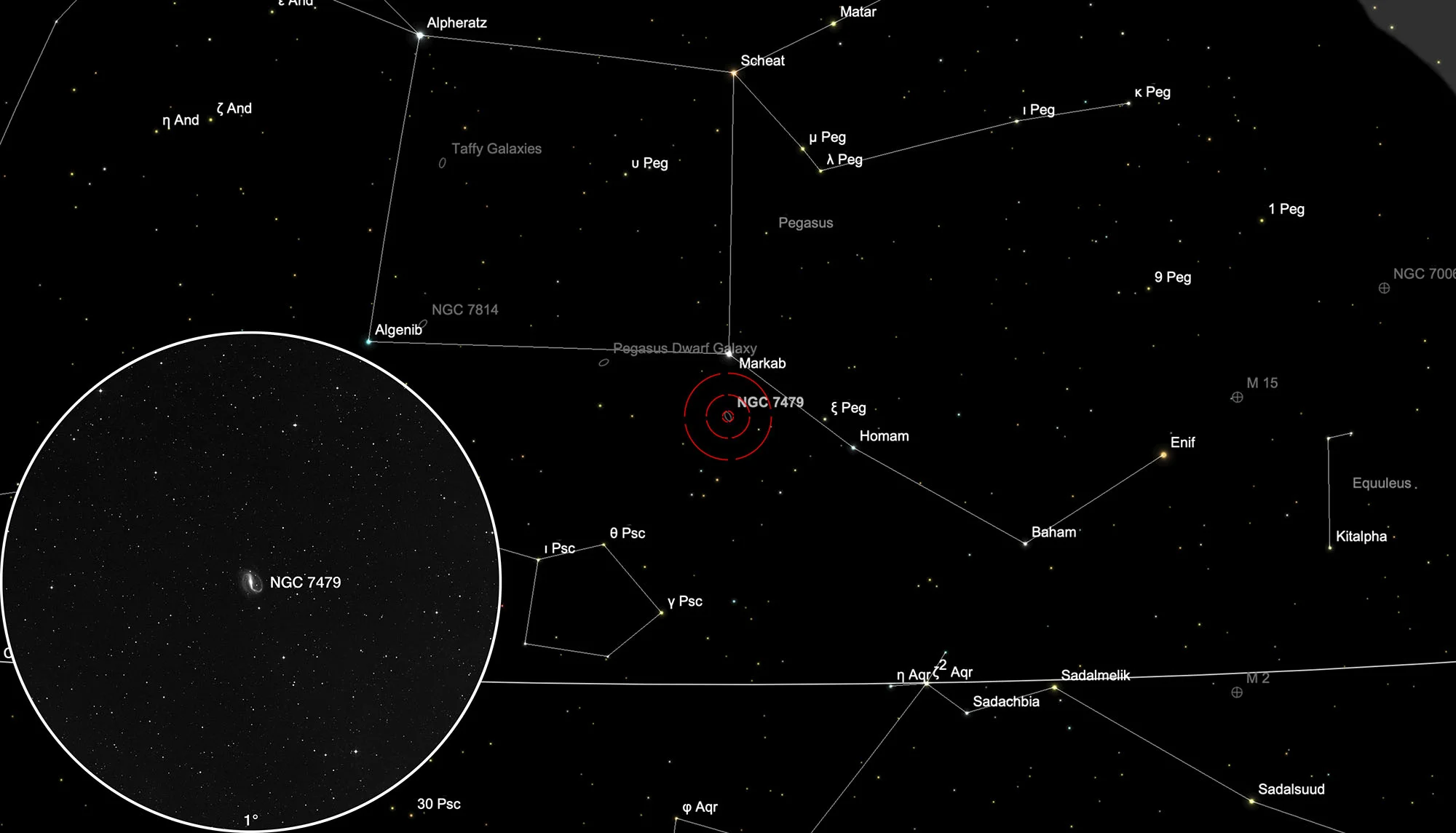
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 7479 is located in the constellation Pegasus and very easy to find: Exaxtly 3° south of the star Markab. On 8 September it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is May to February, when it is highest at night.
Visual Observation
300 mm Aperture: Only the elongated bar of the barred spiral galaxy was visible, which appeared somewhat brighter at the northern end. I could not see anything of the spirals. However, the transparency of the air was not very good either, despite the high altitude on the Titlis. — 300 mm f/4 Popp Newton, Titlis 3020 m. a.s.l., SQM 21.09, 29 October 2022, 22:10, Bernd Nies
320 mm Aperture: Barred spiral galaxy NGC 7479 shows one brighter end of only two spiral arms. — 12.5" Ninja-Dobson f/4.5, Tele Vue Radian 8 mm (181x), 17.-18. Oktober 2001, Hohnegg CH, 1460 m ü. M., Eduard von Bergen