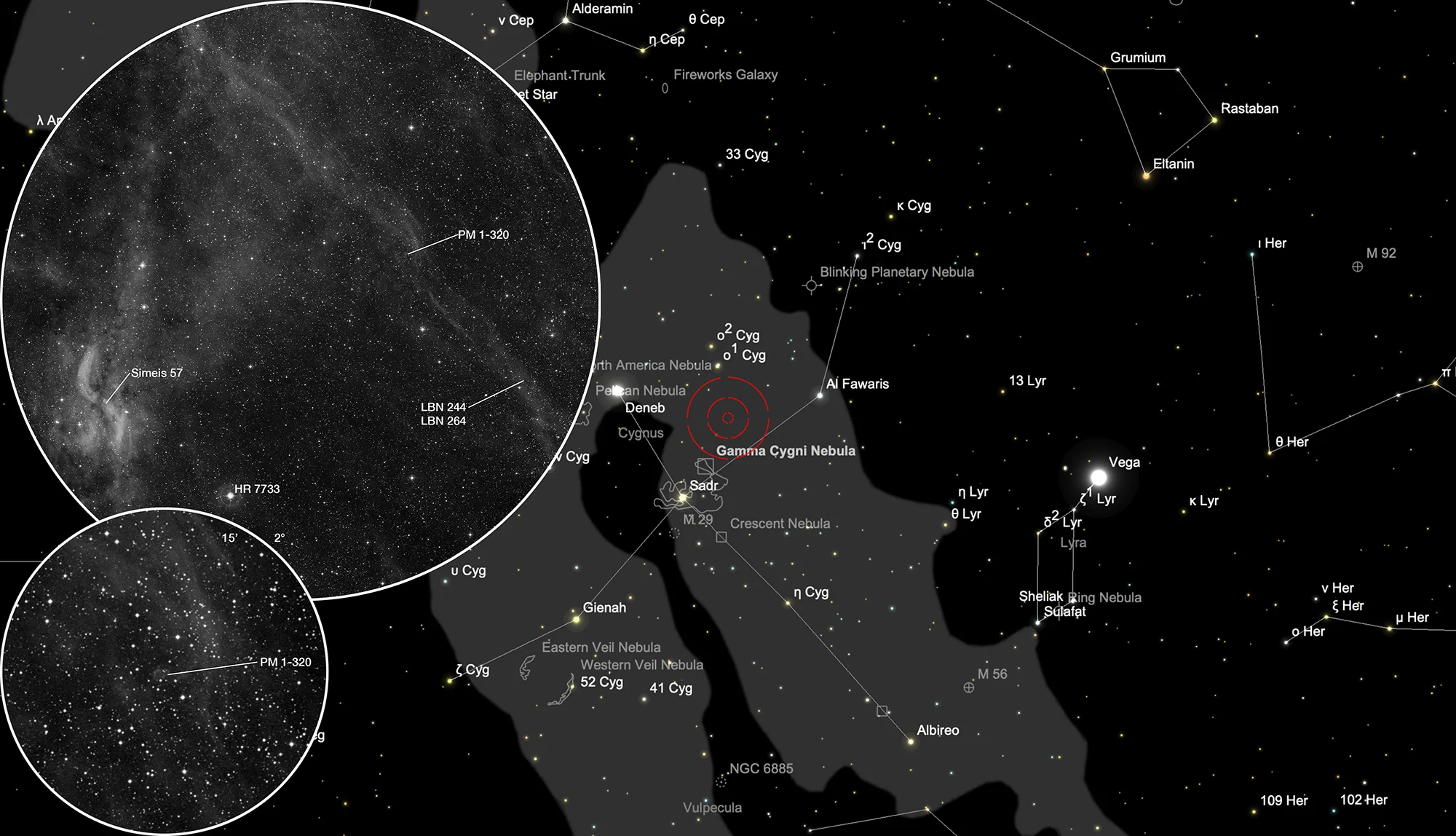
Planetary Nebula Candidate PM 1-320

History
This object was first detected using IRAS (Infrared Astronomical Satellite). Launched on 25 January 1983 for a ten month mission, IRAS was the first space observatory to perform an all-sky survey at infrared wavelengths. The object was listed there as infrared point source IRAS 20088+4402, where the numbers represent the location in B1950 coordinates. In 1988 Andrea Preite-Martinez examined the IRAS Point Source Catalogue and found 340 possible new planetary candidates based on his selection criteria. But 48 of them were already ruled out as suspected non-PN. [741]
Physical Properties
According to Gaia Early Data Release 3 (Gaia EDR3) the parallax of this PN is 0.2717 mas (milli-arcseconds), which corresponds to a distance of 3680 parsec. [145] PM 1-320 appears to be involved in one of the filaments of the H-II regions LBN 244/264 and appear to have caused an excited shockfront in the nebula from an older eruption. There are no detailed studies referenced at CDS, so the PN status is officially uncertain.
| Name | IRAS 20088+4402 |
| Object Type | PN? |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 20h 10m 33s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +44° 11' 57" |
| Parallaxes | 0.2717 mas |
| Magnitudes | G 17.4786; J 14.655; H 13.731; K 12.97 |
| Identifiers | 2MASS J20103261+4411569; Gaia DR3 2081178320846157184; IRAS 20088+4402; WISE J201032.62+441157.2 |
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula candidate PM 1-320 is located in the constellation Cygnus, roughly 1.1° northwest of the Propeller Nebula Simeis 57. On 24 July it is in opposition to the Sun and culminates at local midnight.