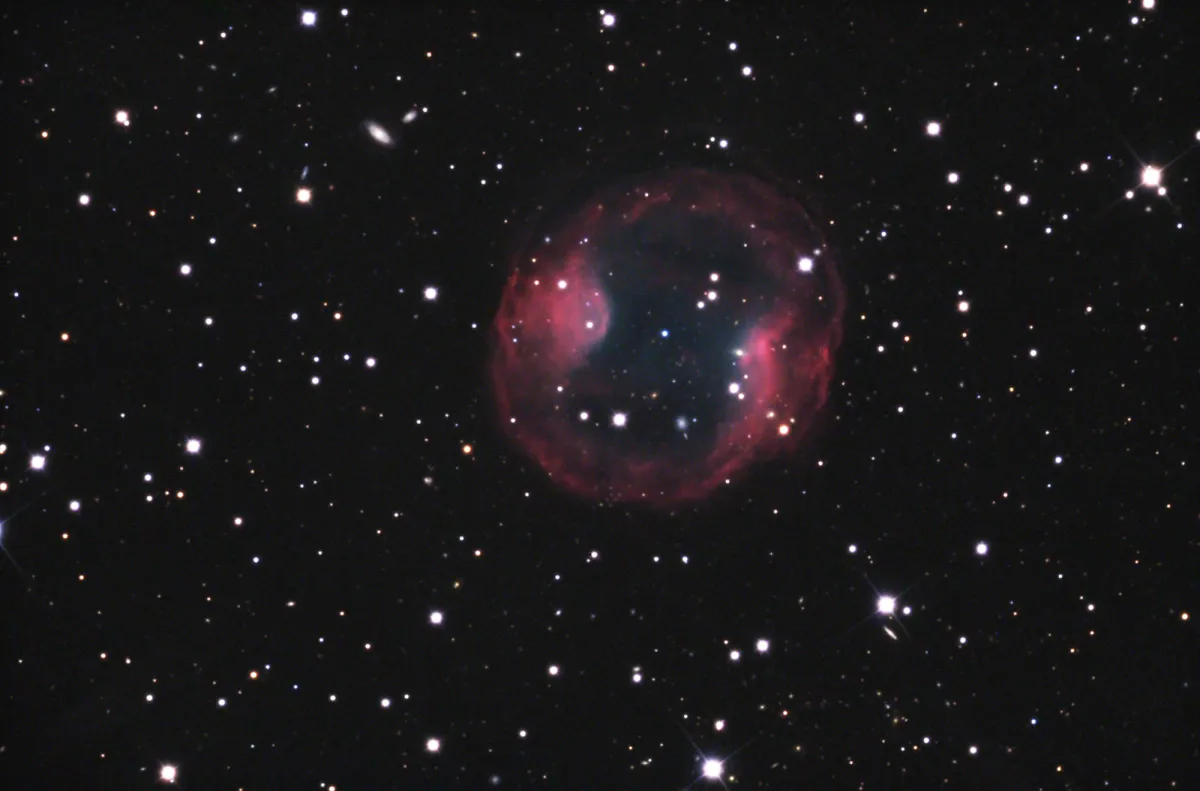
Headphone Nebula (JnEr 1)

History
The planetary nebula Jones-Emberson 1 (JnEr 1, PK 164+31.1, VV 47, VV '74) was discovered in 1939 by the American astronomers Rebecca Jones and Richard M. Emberson on photo plates of the Harvard Observatory. She discovered another planetary nebula that bears her name: Jones 1 (PK 104-29.1) in the constellation Pegasus. [325]
The designation PK 164+31.1 comes from the two Czechoslovak astronomers Luboš Perek and Luboš Kohoutek, who in 1967 compiled a catalog of all the planetary nebulae of the Milky Way known at the time. The designation VV 47 or VV '74 goes back to the Russian astronomer Boris Vorontsov-Velyaminov, who studied and classified planetary nebulae in addition to cataloging galaxies. Because of its appearance, the nebula was also nicknamed «Headphone Nebula». [145]
Physical Properties
JnEr 1 is a 13,000 year old planetary nebula with an angular diameter of about 380 arc seconds and a low surface brightness. In the centre there is a white dwarf star with 0.63 solar masses and 16.8 magnitudes. The apparent visual brightnes of the nebula is 17.1 magnitudes. The distance is 578 pc (around 1800 light years). [145, 325, 326, 327]
| Designations | PN G164.8+31.1: JnEr 1, PK 164+31.1, ARO 121, VV 47, VV' 74 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 07h 57m 53s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +53° 25' 18" |
| Dimensions | 380." (optical) |
| Radial Velocity | -84.3 ± 8.8 km/s |
| Expansion Velocity | 22.0 (O-III) 41. (N-II) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 95 |
| C-Star Magnitude | U: 15.26, B: 16.53, V: 16.83 |
| Discoverer | JONES et al 1939 |
Galaxies NGC 2474 and NGC 2475
The two elliptical galaxies NGC 2474 and NGC 2475 are around 13 magnitudes bright and are located 33 arc minutes south of the planetary nebula JnEr 1. NGC 2474 was discovered on 17 March 1790 by William Herschel and NGC 2475 on 9 January 1856 by RJ Mitchell . The PN is often confused with these NGC numbers, but J. L. E. Dreyer's description clearly fits these two galaxies. [145, 196]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | z | D(z) | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 2474 | 07 58 00.3 | +52 51 44 | Gx (E0) | 14.0 | 13.1 | 0.9 | 12.5 | 0.8 × 0.8 | 0.018623 | 78.66 | F, pS, E ?, bMvS * ?, L * nf | WH III 830; h 471; GC 1591; UGC 4114; MCG 9-13-97; CGCG 262-52; KCPG 147B; NPM1G +52.0051 |
| NGC 2475 | 07 57 58.8 | +52 51 26 | Gx (E0) | 14.2 | 13.2 | 1.0 | 11.8 | 0.6 × 0.6 | 0.018776 | 79.31 | Makes D neb with h 471 | GC 1592; UGC 4114; MCG 9-13-96; CGCG 262-52; KCPG 147A |
Finder Chart
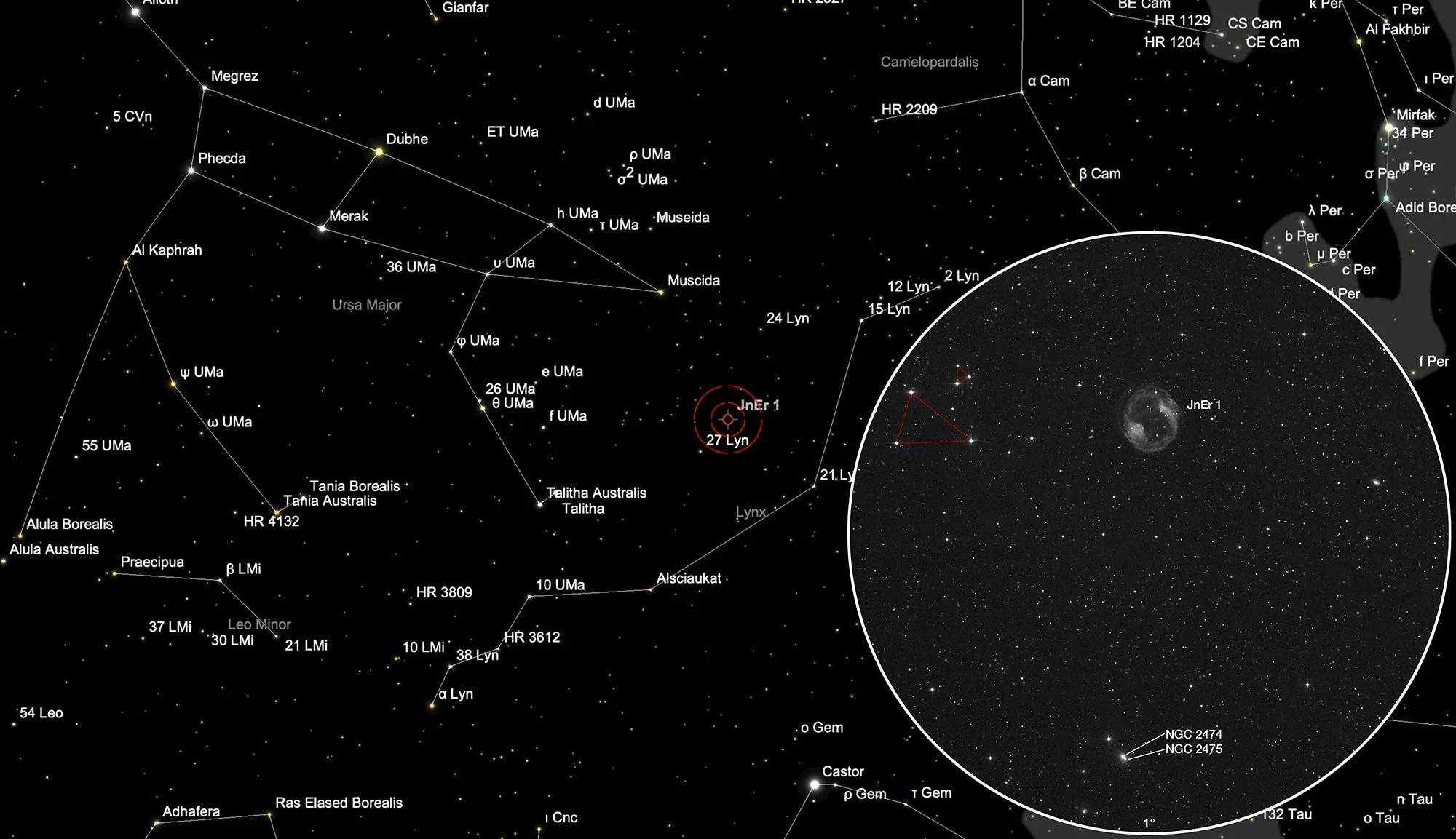
The planetary nebula Jones-Emberson 1 is located in the constellation Lynx, about 2.5 ° northwest of the 4.8 mag bright star 27 Lyncis. It is circumpolar in Central Europe, but the best time to observe it is January to December, when the constellation is highest at night.
Visual Observation
400 mm Aperture: In the 21 mm Ethos eyepiece (85x) and without filter, the position of the PN can be clearly determined thanks to the conspicuous star formation consisting of a large and small triangle. The brightest area of the nebula is just barely discernible without the O-III filter, especially if the image moves a little during search movements. With O-III filter the nebula appears faint and diffuse and a slightly darker centre, overall fainter than Jones 1 in Pegasus. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Ibergeregg, SQM 21.2, 27. 11. 2022, 01:10, Bernd Nies